Cloud Storage Vs Local Storage The Ultimate Comparison Guide
The whole cloud versus local storage debate really just comes down to one question: do you value accessibility and scalability more, or do you need speed and control? There’s no single right answer—it all depends on what you’re trying to accomplish. Local storage gives you instant, direct access to your files, while the cloud offers the freedom to get to your data from anywhere.
Choosing Your Data Storage Solution
When you're weighing cloud against local storage, there's no magic bullet. The "best" choice is the one that lines up with your priorities for cost, security, performance, and accessibility. Each path has its own clear advantages for different kinds of workflows, so it’s worth taking a moment to think it through before you commit.
The fundamental difference is just where your data physically lives. Local storage means your files are on devices you own and can touch, like hard drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), or a Network Attached Storage (NAS) unit in your office. This setup gives you total control and unbeatable speed, perfect for heavy-lifting tasks like editing huge video files or managing sensitive information offline.
On the flip side, cloud storage means you’re entrusting your data to third-party servers you access over the internet. This model has exploded in popularity for a reason. Projections show that by 2025, the cloud will be home to over 100 zettabytes of data, with nearly half of all organizations adopting cloud-first strategies.
For a lot of people, the smartest move isn't picking one over the other, but using both. A hybrid approach lets you use fast local storage for your daily, performance-critical tasks while tapping into the cloud for team collaboration, remote access, and bulletproof disaster recovery. This kind of thinking is at the heart of modern data backup strategies.
If you want to dig even deeper into the nuts and bolts, this excellent local vs. cloud backup guide is a great resource.
Cloud Vs Local Storage At a Glance
To make the decision a bit easier, here’s a quick breakdown of how cloud and local storage stack up on the most important factors.
| Factor | Cloud Storage | Local Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Access files from any device with an internet connection. | Requires physical access to the storage device. |
| Control | Data is managed by a third-party provider. | You have complete physical and digital control. |
| Performance | Speed depends on your internet connection. | Offers the fastest data access and transfer speeds. |
| Scalability | Easily increase or decrease storage capacity on demand. | Requires purchasing new hardware to expand. |
This table gives you a high-level view, but the best choice always comes down to your specific needs—how you work, what you’re storing, and who needs to access it.
Breaking Down the Key Differences
Choosing between cloud and local storage isn't a simple decision. It comes down to a handful of core factors that directly impact your workflow, budget, and peace of mind. To figure out what's right for you, we need to dig into the nuances of cost, security, performance, and scalability. The best solution is rarely the same for everyone; it's all about your specific situation.
This quick visual guide sums up the core strengths of each approach.
As you can see, local storage really shines when it comes to speed and having direct control. On the flip side, the cloud's biggest wins are universal access and pure flexibility.
The Cost Equation: Upfront vs. Ongoing
The way you pay for local and cloud storage couldn't be more different. Local storage is a classic capital expenditure (CapEx). You're buying hardware—hard drives, SSDs, or even a full server—which means a significant cost upfront. Once you've made that investment, your ongoing costs are minimal, usually just electricity and maybe a replacement part down the line.
Cloud storage, however, runs on an operational expenditure (OpEx) model. It's a subscription. This is great for avoiding a big initial spend, making top-tier storage accessible for a predictable monthly fee. But watch out for the hidden costs. Data egress fees, which are charges for downloading your own data, can sneak up on you and become a serious expense, especially if you're constantly moving large files around.
For those who like the idea of owning their hardware but want network access, a NAS device (Network Attached Storage) can be a great middle ground. It’s your own private cloud, right in your home or office.
Security and Data Control: Who Holds the Keys?
Security is probably the most heated debate in the local versus cloud argument. With local storage, you have absolute physical control. The data lives on your hardware, in your building. You are 100% responsible for protecting it from theft, fire, and cyberattacks.
This level of control is a huge plus if you’re handling sensitive information or need to meet strict compliance standards like HIPAA. You manage everything from the locks on the door to the firewall on your network.
Cloud providers use a shared responsibility model. They pour billions into securing their massive data centers with technology and expertise that most individuals or small businesses could never afford. But the key word is "shared." They secure the infrastructure, but you’re still on the hook for managing user permissions, enforcing strong passwords, and configuring your accounts correctly.
Performance and Latency: The Speed Test
This is where physics gives local storage a clear edge. When you open a file from a drive connected directly to your computer, it's almost instant. The data has only a few inches to travel. For demanding tasks like 4k video editing or running complex applications, that low latency is absolutely essential.
Cloud storage performance, on the other hand, is completely at the mercy of your internet connection. Even with a fast connection, there will always be more latency than a local drive. Trying to transfer massive files can be a real time-sink, and a flaky connection can grind your productivity to a halt.
Local Storage Speed Depends On:
- Drive Type: SSDs are worlds faster than traditional spinning hard drives (HDDs).
- Connection: Thunderbolt and USB4 offer much higher transfer speeds than older USB ports.
- Your Computer: Your PC's processor and RAM also play a role in how fast it can access and work with files.
Cloud Storage Speed Depends On:
- Internet Bandwidth: Your upload and download speeds are the biggest factor.
- Provider's Network: How efficient the cloud company's own infrastructure is.
- Distance: It can even be a tiny bit faster if you’re physically closer to their data center.
Scalability: Growing Pains vs. Growing Gains
Scalability is all about how easily you can add more storage when you need it. This is, without a doubt, the cloud's knockout feature. Need more space? A few clicks and your storage plan is upgraded, giving you instant access to terabytes more.
This on-demand model is incredibly efficient. You only pay for what you use, so you're not wasting money on empty drive space you might need someday.
Scaling local storage is a much more hands-on affair. When a drive fills up, you have to physically buy and install a new one. It involves planning, purchasing, and a bit of work. You also tend to overbuy, getting a bigger drive than you need right now just to put off having to do it all again in a few months.
Accessibility and Collaboration: Working Together
In a world of remote work and global teams, being able to access files from anywhere is critical. The cloud was built for this. Your data is available on your laptop, tablet, or phone, as long as you have an internet connection.
This is what makes modern collaboration possible. Multiple people can edit the same document at the same time, seeing changes live. It’s why platforms like Google Drive and Dropbox have become the backbone of so many businesses.
Local storage is, by design, tied to a physical place. While you can set up remote access to a local server, it's often clunky and requires some technical know-how. Real-time collaboration is much harder and usually involves emailing files back and forth—a recipe for version-control chaos.
Analyzing the Real Cost of Data Storage
When you’re weighing cloud vs. local storage, the price tag is usually the first thing you look at. But that initial number almost never tells the whole story. The true cost goes way beyond a monthly subscription or the price of a new hard drive. To make a smart financial decision, you have to dig into the total cost of ownership.

With local storage, you’re looking at a big upfront investment in hardware. It's a predictable capital expense, but it can be a hefty one. Cloud storage flips that model on its head with a low-cost, pay-as-you-go approach. The catch? Those recurring operational costs can add up—and sometimes spiral out of control if you're not careful.
Calculating the Total Cost of Local Storage
That price you pay for a new hard drive, SSD, or Network Attached Storage (NAS) device? That's just the starting line. The total cost of ownership (TCO) for local storage includes a bunch of ongoing and often-hidden expenses you absolutely have to factor in.
Remember, these costs are spread out over the lifespan of your gear, which is typically 3-5 years for hard drives before they wear out and need to be replaced.
Here’s what you need to add up for your local storage TCO:
- Initial Hardware Purchase: This is the most obvious cost. It can be less than a hundred dollars for an external drive or run into the thousands for a serious multi-bay NAS system.
- Ongoing Electricity Consumption: Storage devices, especially those always-on NAS units, are constantly sipping power. It adds a small but consistent amount to your utility bills.
- Maintenance and Replacements: Hardware fails. It’s not a matter of if, but when. You have to budget for replacing drives, cooling fans, or eventually the entire unit.
- Upgrade Cycles: As your data grows, you'll eventually need bigger drives or a more powerful system. This kicks off another round of capital investment.
Key Takeaway: Local storage is a capital expense with predictable, if lumpy, costs. The biggest hit to your wallet is at the beginning, followed by smaller ongoing expenses for power and eventual replacements.
Unpacking Hidden Cloud Storage Fees
Cloud storage pricing looks deceivingly simple at first. You pay a set fee each month for a certain amount of space. Easy, right? The real costs, however, are often buried in the fine print—especially for anyone dealing with large files or high-volume workflows.
The most notorious hidden cost is data egress fees. Uploading your data to the cloud is almost always free. But when you need to download it or move it somewhere else, the provider charges you. For a video production team that’s constantly pulling down massive project files for editing, these egress fees can easily blow past the base subscription cost. Suddenly, local storage for active projects starts looking a lot cheaper.
Beyond egress, other charges can quietly inflate your monthly bill:
- API Request Charges: Some providers charge for how many times your apps "talk" to their storage, which can be a surprise cost for automated workflows.
- Tiered Pricing Complexities: Go over your storage tier, and you could face significant overage charges, often at a much higher per-gigabyte rate.
- Data Transfer Speeds: Moving large files frequently doesn't just cost money; it costs time. You can use our handy file transfer time calculator to get a better sense of how long these operations will take so you can plan for them.
The pay-as-you-go model offers amazing flexibility, but it demands constant monitoring to keep costs in check. For a small business with predictable, archive-heavy storage needs, the cloud's low barrier to entry might be perfect. But a creative agency pushing terabytes of data every month could find those variable costs completely unsustainable. It all comes down to your specific usage patterns.
Evaluating Security and Data Control
When it comes to your data, security is everything. The whole “cloud vs. local” debate often frames this as a simple choice between control and convenience, but that’s not the full picture. It's easy to assume local storage is automatically safer, but the reality is much more nuanced. Both models come with their own set of security responsibilities, and the right choice really boils down to your resources, expertise, and just how sensitive your data is.
With local storage, the security burden is 100% on you. You’re the gatekeeper, responsible for everything from physically protecting the hardware to defending it from digital threats. That means locking down your devices from theft, setting up firewalls, managing encryption, and having a bulletproof backup plan.
This total control can be a huge plus, but it also means any security slip-up is on you. The most common weak points are pretty straightforward: physical theft of a hard drive, hardware failure that wipes out your data, or a ransomware attack that locks up every single one of your files.
The Shared Responsibility Model of Cloud Security
Cloud storage, on the other hand, runs on what’s called a shared responsibility model. This isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a framework that splits security duties between you and the cloud provider. Think of it as a partnership where both sides have a critical role to play.
Big players like Amazon Web Services, Google, and Microsoft pour billions of dollars a year into securing their infrastructure. They have teams of elite security experts and deploy threat detection systems that are way beyond what most individuals or even small companies could ever afford.
Here’s what they typically handle:
- Physical Security: Protecting data centers with Fort Knox-level security, including biometric scanners, 24/7 surveillance, and backup power systems.
- Infrastructure Security: Locking down the servers, networks, and software that run the whole cloud operation.
- Compliance and Certifications: Meeting tough international standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. This makes life much easier for businesses that need to follow strict regulations.
Your job in the cloud is to secure your data within their fortified environment. This means managing access, using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, and maybe even encrypting your files before you upload them.
Data Privacy and Sovereignty Considerations
Even with the cloud provider's top-notch security, you still have to think about where your data is physically located. Data sovereignty is the legal concept that your data is subject to the laws of the country where it’s stored. This is a massive deal for any business handling personal information or working in places with strict privacy laws.
It’s crucial to pick a provider that lets you choose the geographic region where your data lives. This helps you stay compliant with local rules, like the GDPR in Europe. For organizations working with highly sensitive data, digging into comprehensive enterprise data security solutions is non-negotiable to ensure you're protected and compliant no matter where your data is stored.
In the end, it’s a classic trade-off. Local storage gives you absolute physical control but demands a lot of expertise and constant vigilance on your part. Cloud storage gives you access to world-class security, but you have to trust a third party and be diligent about your side of the shared responsibility deal. For most people, the advanced security and built-in compliance from major cloud providers offer a level of protection that would be incredibly expensive and difficult to build on their own.
Best Use Cases for Cloud and Local Storage
All the theory is great, but the real test for cloud vs. local storage happens in day-to-day work. Figuring out where each one truly excels is what makes the decision simple. It’s less about one being better overall and more about which is the perfect fit for a specific job.
Let's walk through a few common scenarios. Seeing how these factors play out in the real world will help you match the right storage to your own workflow.
When Local Storage Is the Clear Winner
Local storage really shines when speed, security, and offline access are absolute must-haves. Some tasks are just impractical—or even impossible—without having your data physically right there with you.
Here are a few situations where keeping it local is king:
- High-Resolution Video Editing: A creative pro editing 4K or 8K video needs instant access to enormous files. The near-zero latency of a local SSD makes scrubbing through timelines and playing back footage buttery smooth. Trying to do that over even the fastest internet connection would be an exercise in frustration.
- Storing Highly Sensitive Data: Think about an R&D department working on a top-secret formula or a law firm handling confidential client files. They simply can't afford any risk of exposure. Local storage creates an "air-gapped" level of security, giving them total physical control over who can touch that critical data.
- Offline Work Environments: Field researchers, photographers on a remote shoot, or anyone working where the internet is spotty depend on local storage. They can access, edit, and save their work without a connection, ensuring a bad Wi-Fi signal never grinds their productivity to a halt.
Key Insight: Local storage is the undisputed champion for performance-heavy tasks and workflows where you need absolute control over your data. If your job involves massive files and demands instant response times, nothing beats having it right there with you.
Scenarios Built for the Cloud
On the flip side, cloud storage is the engine of modern collaboration and on-the-go access. Its power lies in connecting people and data seamlessly across different locations and devices. When sharing and universal access are the top priorities, the cloud is the undeniable winner.
These are the use cases where the cloud is the perfect tool:
- Collaborative Team Projects: A marketing team spread across different time zones all need to chip in on the same presentation. Cloud platforms like Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive allow for real-time co-editing. This means everyone is always working on the latest version, killing off those dreaded version control nightmares for good.
- Remote Workforce Accessibility: For any company with a distributed team, the cloud is non-negotiable. It acts as a central, secure hub for all company documents, making sure every employee can get the files they need to do their job, no matter where they’re logging in from.
- Off-Site Backup and Disaster Recovery: Businesses of all sizes lean on the cloud for reliable backups. Storing copies of critical data off-site protects against local disasters like a fire, flood, or even theft. It's the cornerstone of any solid business continuity plan, ensuring you can get back up and running quickly after the unexpected happens.
In the end, this isn't about picking a side and sticking to it forever. It's about strategically choosing the right tool for the job. Many professionals find a hybrid approach works best—using local storage for active, high-performance work and the cloud for collaboration, sharing, and archiving. That balance often offers the best of both worlds.
The Rise of Hybrid Storage Solutions
The whole “cloud vs. local storage” debate often paints a picture of having to pick one side. But more and more, businesses and professionals are realizing the smartest move isn't to choose one, but to combine them. This approach, known as hybrid storage, isn't about compromise; it’s a strategic play that gives you the best of both worlds.
This blend of on-site hardware and off-site cloud services has quickly become a go-to for data management. It's not a niche trend, either. A remarkable 77% of organizations are already running a hybrid model or plan to adopt one soon, showing a major shift away from setups that are purely local. You can explore the findings of the 2025 hybrid cloud report to see just how deep this trend runs.
How Hybrid Storage Works in Practice
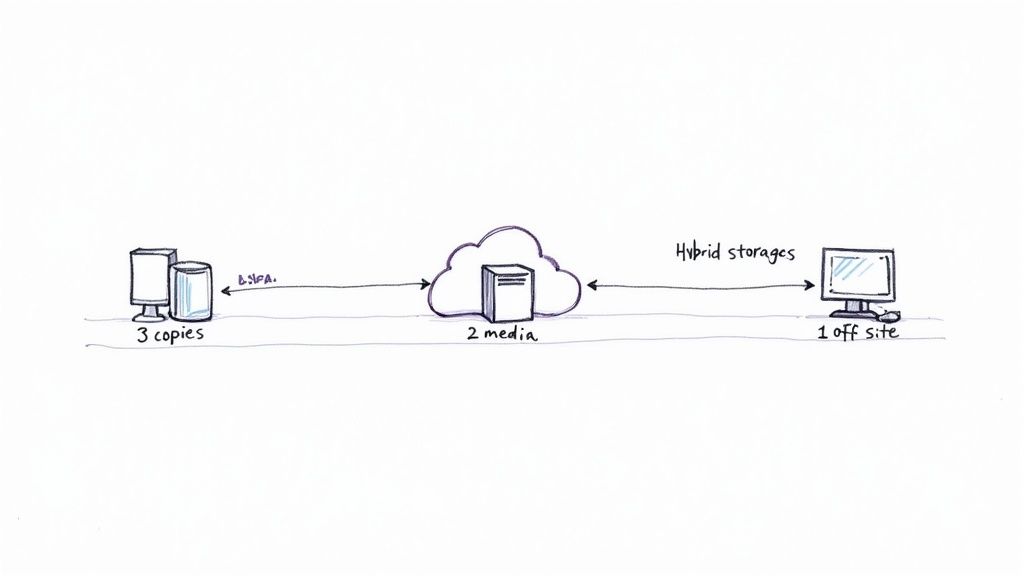
At its heart, a hybrid model uses your local hardware for speed and instant access, while leaning on the cloud for backup, resilience, and collaboration. The classic example of this in action is the "3-2-1 backup" strategy—pretty much the gold standard for keeping data safe.
This rule is simple:
- Keep three total copies of your important data.
- Store these copies on two different types of media.
- Make sure one of those copies is located off-site.
In a hybrid setup, this translates to keeping your primary working files on a local drive, a second backup on another local device (like a NAS), and a third copy synced to the cloud. This gives you solid redundancy against just about anything—hardware failure, theft, or a local disaster.
By combining local speed with cloud resilience, hybrid storage moves beyond a simple backup plan. It becomes an active, flexible system that adapts to your workflow, providing both performance and peace of mind.
Scenarios Where Hybrid Shines
The real magic of a hybrid approach shows up in real-world workflows that need both raw performance and easy access. This isn't just for big companies; it's an incredibly practical solution for all kinds of professionals.
Creative Agencies: Imagine a video editor working with massive 4K project files. They need to edit directly from a high-speed local SSD or NAS for a seamless, lag-free experience. Once the final cut is approved, they can compress it with a tool like Compresto and upload the smaller file to the cloud for the client to review and download from anywhere.
Financial Services: A firm needs to process a high volume of transactions on a secure, low-latency local server to guarantee speed and data privacy. At the end of the day, that data gets automatically archived to a compliant cloud service for long-term storage, meeting regulatory needs without clogging up expensive primary systems.
Ultimately, a hybrid solution acknowledges a simple truth: no single storage type is perfect for every task. It lets you strategically put your data where it serves you best—right in front of you for active work, and safely in the cloud for everything else.
Frequently Asked Questions
Thinking through the cloud vs. local storage debate always brings up a few key questions. Let's tackle the most common ones head-on.
Is Cloud Storage Really Cheaper Than Local Storage?
Not always. The cloud looks cheaper upfront because you skip the big hardware purchase. But those monthly subscriptions and data transfer fees can really add up over time, especially if you're constantly moving large files around.
When you look at the total cost of ownership over 3–5 years, local storage can actually come out ahead. Think of it this way: the cloud is cheaper to start, but local can be cheaper to own in the long run.
Can I Get Hacked More Easily on the Cloud?
It’s a valid concern, but the risk is just different, not necessarily greater. Cloud providers pour massive resources into security, with teams of experts defending their servers against major attacks. Where things usually go wrong is on the user's end—think weak passwords or accidentally making a private folder public.
Local storage, on the other hand, is vulnerable to physical theft or direct attacks on your home network if you haven't secured it properly.
Security Takeaway: Cloud security is a partnership. The provider secures the infrastructure, but you're responsible for securing your own account and controlling who can access your data.
What if My Internet Goes Down?
This is the Achilles' heel of any cloud-only setup. No internet means no access to your files. Period. It can bring your entire workflow to a screeching halt.
Local storage is completely immune to this problem. Your files are right there, on your machine, ready whenever you need them. For anyone with spotty internet or critical work that can't be interrupted, local access is non-negotiable.
Is It Possible to Lose My Files in the Cloud?
While it’s incredibly rare, it's not impossible. Data loss could happen because of an account issue or, in a worst-case scenario, a failure on the provider's side.
However, the big cloud services build in serious redundancy, meaning they store copies of your data in multiple physical locations to prevent exactly that. Honestly, you're far more likely to lose data from a single local hard drive failing without a proper backup strategy in place.
Ready to optimize your local storage and make sharing easier? Compresto compresses your videos, images, and documents directly on your Mac, reclaiming valuable disk space and speeding up file transfers—no cloud needed. Learn more at https://compresto.app.