How to Compress Files for Email Effortlessly
Why Email Attachment Limits Are Sabotaging Your Workflow
Sending large files via email can be a frustrating experience. You write the perfect email, attach the necessary files, and hit send, only to receive an error message about exceeding attachment size limits. This isn't just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly disrupt your workflow. Why do these limits exist? The reasons are more complex than simply limited storage space on email servers.
These size restrictions primarily protect email deliverability and prevent your emails from being flagged as spam. Large attachments can overload email servers, slowing down delivery times for everyone. Spam filters often view large attachments suspiciously, potentially diverting your important emails to the spam folder. Even if your email sends successfully, it might not reach your recipient's inbox.
Large attachments also mean slower send times for you and slower download times for your recipients. Imagine sending a large video file – the upload alone can take considerable time, tying up your computer's resources. Downloading that file can be equally time-consuming for recipients, especially those with slower internet connections. This impacts productivity for everyone involved. Consider checking out this helpful resource: How to master email attachment size limits
Email deliverability is a major concern, especially for businesses that rely heavily on email communication. By 2025, average inbox delivery rates for business emails declined across major providers, with some experiencing decreases of 10% or more. Almost half of all emails are classified as spam, highlighting the need to manage file sizes through compression. For more detailed statistics, see this blog post.
Ultimately, compressing files before emailing is crucial for maintaining a good sender reputation and ensuring your messages reach their destination. Reducing file sizes improves deliverability and contributes to a smoother, more efficient email experience for everyone.
Mastering Compression Techniques That Actually Work
Stop wrestling with oversized email attachments. This section explores effective compression strategies for sending files via email, ensuring your messages arrive swiftly and reliably. Whether it's documents, images, videos, or a mix of file types, understanding compression is crucial.
Lossless vs. Lossy Compression: Choosing the Right Approach
Lossless compression shrinks files without losing any data. It's like organizing a suitcase efficiently – everything fits, just more compactly. This is perfect for documents and spreadsheets where preserving all information is vital. Lossy compression, conversely, discards some data to achieve smaller sizes. Imagine summarizing a lengthy article – you retain the core points, but some details are lost. Lossy compression suits images and videos where minor quality changes are often unnoticeable.
Optimizing Compression for Different File Types
Different file types respond differently to compression methods. Text files, like Word documents, compress remarkably well with lossless methods like ZIP, often shrinking by 50% or more. Image files, particularly JPEGs, handle lossy compression without significant visual impact. Specialized image compression tools can yield substantial size reductions. Videos, typically the largest files, benefit from advanced compression codecs that minimize size while maintaining reasonable quality. Understanding these distinctions allows you to tailor your compression strategy.
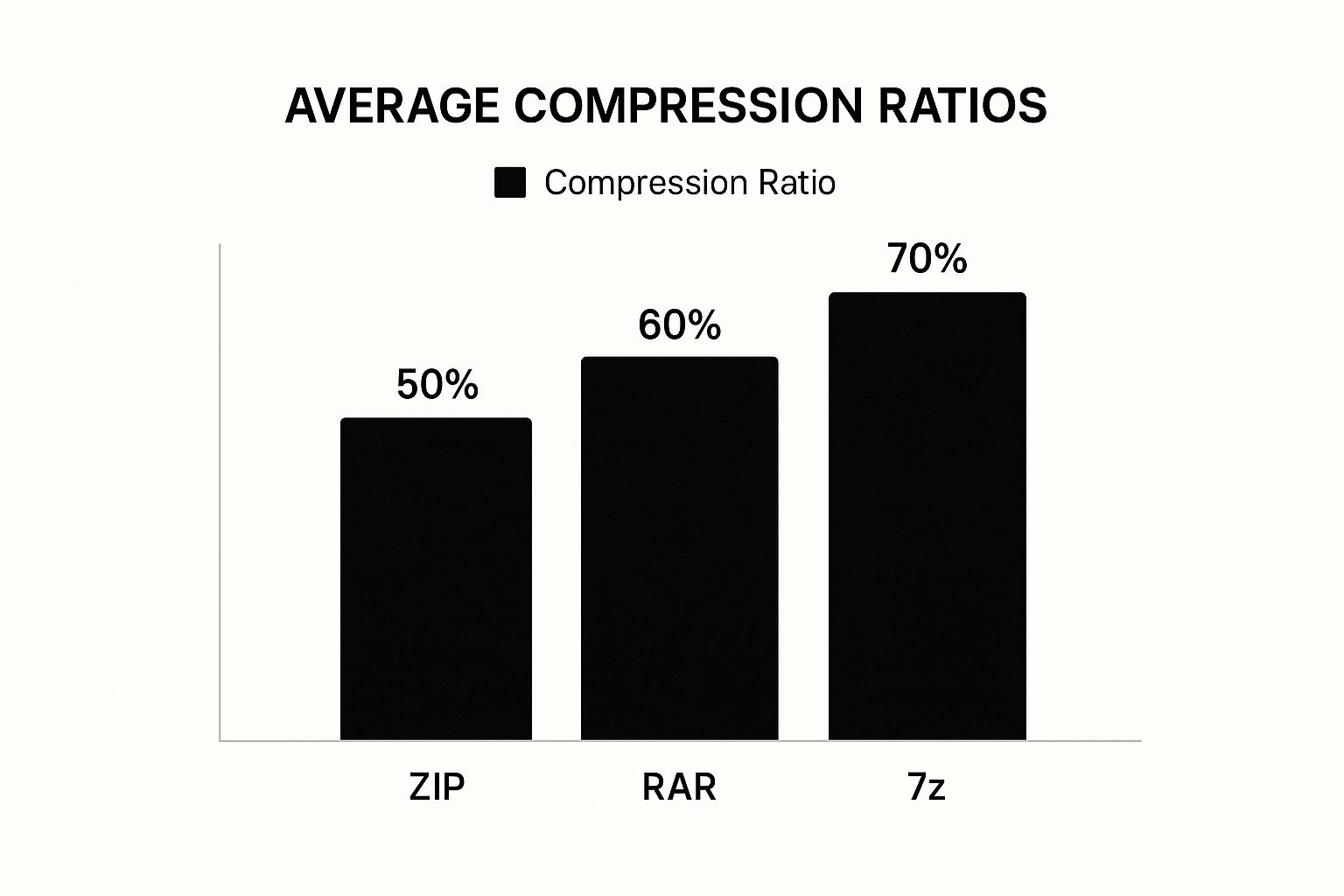
The infographic above shows average compression ratios of common archive formats. 7z offers the highest compression at 70%, followed by RAR at 60%, and ZIP at 50%. The right format depends on balancing compression and compatibility with the recipient's software.
To further illustrate the impact of different compression techniques and formats, consider the following table:
Compression Results by File Type Comparison of compression ratios achieved with different file formats using standard compression tools.
| File Type | Original Size | Compressed Size (ZIP) | Compression Ratio (ZIP) | Quality Impact | Compressed Size (7z) | Compression Ratio (7z) | Quality Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text Document (.docx) | 10MB | 2MB | 80% | None | 1.5MB | 85% | None |
| Image (.jpg) | 5MB | 3MB | 40% | Minimal | 2MB | 60% | Minimal |
| Video (.mp4) | 100MB | 70MB | 30% | Noticeable | 50MB | 50% | Noticeable |
This table demonstrates that text documents compress the most effectively, followed by images and then videos. While 7z often offers higher compression, the difference might be less noticeable for certain file types like images.
Advanced Compression Techniques: Maximizing Efficiency
Beyond the basics, advanced techniques further optimize compression. Selective compression targets only the most compressible files, saving time and resources. Batch processing automates compression for multiple files, streamlining the process. Adjusting settings within your chosen tool fine-tunes the balance between size and quality. These advanced strategies are particularly useful for IT professionals or anyone handling large files regularly.
Email continues to be a primary communication tool, making efficient file management increasingly important. By 2025, global email users reached 4.83 billion, projected to rise to 5.61 billion by 2030. This underscores the need to optimize email attachments. Learn more about this growth here. Tools like WinZip help address these challenges, offering significant compression across various formats. As email usage expands, especially in fields exchanging large files, using advanced compression tools will likely increase.
Choosing The Right Compression Tools For Your Needs
Navigating the world of compression software can feel overwhelming. This section offers practical advice on selecting the best tools for compressing files, especially for email, cutting through the marketing jargon.
Popular Compression Tools: A Comparative Overview
Several well-established compression tools consistently deliver excellent results. 7-Zip, a free and open-source option, is known for its high compression ratios and broad format support. 7-Zip is a great choice for users prioritizing efficiency. WinRAR, a popular choice for both general and professional use, is known for its reliability and advanced features like error recovery. WinRAR is a solid all-around option. WinZip, a long-time favorite, offers a user-friendly interface and integrates seamlessly with Windows. WinZip prioritizes ease of use for Windows users.
Newer cloud-based and platform-specific tools are also emerging. For macOS users, Compresto offers specialized features for video and image compression, making it perfect for sharing and storing large media files. Compresto caters to content creators on macOS. These newer tools often specialize in specific file types and workflows.
Here's a table summarizing the key features and best uses of each tool:
| Tool | Platform | Price | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-Zip | Windows, Linux, macOS | Free | High compression ratios, open-source | Users prioritizing compression efficiency |
| WinRAR | Windows, macOS, Linux | Paid | Reliability, error recovery, multiple formats | General and professional use |
| WinZip | Windows, macOS | Paid | User-friendly interface, Windows integration | Ease of use, Windows users |
| Compresto | macOS | Paid | Video/image optimization, macOS integration | macOS users, content creators |
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors to Consider
The ideal compression tool depends on your specific needs. If maximum compression is your priority, 7-Zip often delivers the best results. For ease of use and seamless Windows integration, WinZip is a strong contender. If you primarily work with large video or image files on macOS, Compresto could be the best fit. Here are some other important factors to keep in mind:
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your operating system.
- Batch Processing: This feature is essential for efficiently handling multiple files.
- Integration with Email Clients: Simplifies the process of sending compressed files via email.
- Security Features: Crucial for protecting sensitive documents.
Hidden Features in Existing Tools
Your current operating system might already offer basic compression features. Both File Explorer in Windows and Finder in macOS have built-in compression capabilities. While they may not be as powerful as dedicated tools, they provide a convenient option for simple tasks.
For example, in File Explorer, you can right-click a file or folder and select "Send to" a "Compressed (zipped) folder." macOS's Finder provides similar functionality. These features are surprisingly helpful for quick email compression tasks without needing extra software.
Mobile and Browser-Based Options
Mobile apps like Compress Photos & Pictures offer compression on the go. Browser-based tools, such as ShortPixel's online image compressor ShortPixel, provide convenient compression without software installation. These options offer flexibility for users who need to compress files on different devices. Choosing the right tool helps you manage file sizes effectively for smooth and successful email communication.
Step-By-Step File Compression For Maximum Results
Sending files via email often requires shrinking them down first. But how you compress a file depends on what kind of file it is. This guide offers practical tips for compressing different file types effectively.
Compressing Documents and Spreadsheets
For Word docs (.doc, .docx) and Excel spreadsheets (.xls, .xlsx), lossless compression is best. This method shrinks the file without losing any data.
- Built-in Compression: Right-click the file, select "Send to," then "Compressed (zipped) folder."
- Higher Compression: For smaller files, use 7-Zip. The
.7zformat often compresses more than standard.zip.
Compressing Images
Image files, especially .jpg, can often be compressed significantly. Lossy compression, which slightly reduces image quality to shrink the file substantially, is a useful option. Just be aware of the balance between quality and size.
- Online Tools: ShortPixel and other online tools offer simple compression without needing software.
- Image Editing Software: For greater control over compression settings, use dedicated image editing software like GIMP or Photoshop.
Compressing Videos
Videos typically require the most attention when compressing for email.
- Reduce Resolution: If high-definition isn't essential, lowering the resolution (e.g., from 1080p to 720p) makes a big difference.
- Video Compression Software: HandBrake offers detailed control over compression settings and codecs, allowing you to balance quality and size. See also: How to master video compression for email.
Handling Multiple Files
Sending many files? Create a ZIP archive to combine everything into one compressed file.
- Select the files.
- Right-click and choose "Send to" then "Compressed (zipped) folder."
- Password Protection: Tools like 7-Zip and WinRAR can create password-protected archives for extra security.
Advanced Techniques
Here are some additional compression strategies:
- Batch Compression: Automate the process for many files at once using the batch features in most compression tools.
- Preserve Folder Structure: When archiving files from multiple folders, ensure the archive retains the original folder organization.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes, problems arise when compressing files. If a recipient can’t open a compressed file:
- Resend: The file might have been corrupted during transfer.
- Different Format: Try
.zip, which is widely compatible. Formats like.7zor.rarmight require specific software. - Check Compatibility: Confirm the recipient has up-to-date software that can handle the compressed file.
By following these guidelines, you can efficiently compress files for email, ensuring smooth delivery and better communication. Choose the method that suits your file type and specific requirements. With a bit of practice, you’ll easily select the right strategy for every situation.
Smart Alternatives When Compression Falls Short
Sometimes, even with the best compression techniques, your files are still too big for email. But don't worry, there are other ways to get those large files to your recipients. Let's explore some practical alternatives.
Cloud Storage Solutions: Sharing Large Files With Ease
Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive offer a great way to share large files. Instead of attaching a file directly, you share a link to the file stored in the cloud. This avoids email attachment size limits completely. Plus, cloud storage often includes version control and collaboration features, which are very helpful for group projects. It's like sending a map to the treasure, not the treasure itself.
Imagine needing to send a 2GB video. Attaching it directly to an email probably won't work. Uploading it to Google Drive and sharing the link lets recipients download it when they're ready, without overflowing their inboxes.
For more tips on making files smaller for email, see this helpful guide: How to reduce file sizes for email attachments.
Specialized File Transfer Services: Security and Control
For added security or extremely large files, consider specialized file transfer services. Many services are designed specifically for this purpose, offering features like encryption and access control. This is especially important for sensitive information. Many services also offer tracking and delivery confirmation, so you know your files have arrived.
Professional Communication: Setting Expectations Clearly
When using these alternatives, be upfront with your recipients. Explain why you're using a cloud link or file transfer service. This avoids confusion and keeps your workflow professional. A simple message like, "This file is large, so I've shared it via Dropbox," can make a big difference.
The sheer volume of emails we handle today presents significant storage and management challenges, especially for businesses. We generate sixty billion new emails daily, and these emails hold over half of all confidential business information. This underscores the need for effective archiving and compression strategies. For more insights, check out these email archiving statistics. The growth of the email archiving market reflects this growing need for efficient solutions.
Hybrid Approaches and Future Trends
Combining compression with cloud sharing can be a powerful strategy. Compressing files before uploading them to the cloud saves storage space and reduces upload times. Another option is splitting large projects into smaller, compressed files and sending them across multiple emails.
Technology continues to advance, bringing new ways to share large files. Staying informed about these developments will help you stay efficient. Explore the available options, try them out, and see what fits your workflow best. This proactive approach will make sharing large files smooth and simple.
Optimizing For Different Email Providers And Platforms
Each email provider handles attachments a little differently. What works perfectly on Gmail might not on Outlook or Apple Mail. This section explains how to optimize your compressed files for various email platforms, making sure delivery is smooth and access is easy for everyone.
Gmail: Leveraging Google Drive Integration
Gmail often works with Google Drive for large files. If you attach a large file, Gmail might suggest uploading it to Drive and sharing a link. This gets around attachment size limits and simplifies sharing big files. This is especially helpful for files over Gmail's 25MB limit.
Outlook: OneDrive Connectivity and Smart Attachments
Outlook connects similarly with OneDrive. Outlook's "smart attachment" feature even suggests OneDrive files based on your email content. If you’re discussing a proposal, Outlook might suggest the latest version from your OneDrive. This saves you the trouble of finding and attaching files manually.
Apple Mail: Attachment Handling and Compatibility
Apple Mail usually handles compressed files well, but issues can arise if recipients use older email clients. Using common compression formats like .zip helps avoid this. Also, use clear file names and extensions inside the archive so recipients easily identify what’s inside.
To get a clearer picture of these differences, let's look at a quick comparison:
| Email Provider | Max Attachment Size | Cloud Integration | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail | 25MB | Google Drive | Automatic Drive link for large files |
| Outlook | 20MB | OneDrive | Smart attachment suggestions |
| Apple Mail | Varies | iCloud | Generally good compressed file handling |
To help illustrate how email clients may appear, here is a visual representation:
This table highlights the key differences in attachment handling across these major email providers. It’s important to remember these variations to avoid potential problems.
Ensuring Cross-Platform Compatibility
When compressing files for email, think about the recipient’s email client and operating system. Standard formats like .zip ensure compatibility. Avoid less common formats like .7z or .rar, as recipients might not have the right software. Sticking to the basics prevents frustrating situations.
Here are a few best practices for cross-platform email attachments:
-
Use Standard Formats:
.zipis usually the best choice. -
Test Your Archives: Open the compressed file on different devices and email clients before sending important files.
-
Provide Clear Instructions: If you must use an uncommon format or a cloud sharing link, explain clearly how to access the files.
By understanding these guidelines and how different email providers work, you can ensure your compressed files reach their destination reliably. This saves you time and frustration, ensuring your communication stays smooth.
Key Takeaways

Sending large files by email can be tricky. It depends on understanding file size limits and using the right techniques. This guide provides a roadmap for compressing files effectively, ensuring your emails arrive without issues.
Essential Compression Techniques
-
Choose the Right Format: For important documents, use lossless compression like .zip, which preserves all data. If some quality loss is okay (like for images or videos), lossy compression is a good choice.
-
Optimize by File Type: Text files compress easily. Images benefit from specific image optimization tools. Videos might require lowering the resolution or using special codecs.
-
Batch Process: If you have many files, automate compression with tools like 7-Zip or WinRAR. This saves a lot of time and effort.
Tool Recommendations
-
7-Zip: A free, open-source tool known for its high compression rates and support for many file formats.
-
WinRAR: A solid choice for general compression, with extra features like error recovery.
-
WinZip: Easy to use, especially if you're on Windows.
-
Compresto: Designed for macOS, particularly effective for optimizing videos and images.
Alternative Strategies When Compression Isn't Enough
-
Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive let you share large files via links.
-
File Transfer Services: Consider these for very large files or when you need extra security.
-
Communicate Clearly: Let recipients know how you're sending the files to avoid any confusion.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
Corrupted Archives: Try resending the file. Make sure the recipient has the right software to open it.
-
Compatibility Problems: Using standard formats like .zip is usually safest. Test your compressed files before sending them, especially to people using different operating systems.
-
File Size Still Too Large: If compression isn't enough, cloud storage or file transfer services are the best alternatives.
By using these tips, you can create a reliable system for sending files by email. From choosing the right compression method to troubleshooting problems, these strategies will help you manage file sizes and make sure your messages get through. Ready for simpler file compression on your Mac? Download Compresto and streamline your workflow.