What Is File Compression and How Does It Actually Work?
File compression, at its heart, is about making digital files smaller by smartly getting rid of the fluff. Imagine trying to pack for a big trip. Instead of just stuffing your bulky winter comforter into a suitcase, you use one of those vacuum-seal bags. You suck all the air out, and suddenly, the same comforter takes up a tiny fraction of the space.
That’s exactly what file compression does, but for your data.
The Big Picture of File Compression
Think of compression as a digital decluttering service for your files. Whether it's a massive video file, a high-res image, or a simple document, special rules called algorithms scan the data for patterns and redundant information. They then figure out clever ways to rewrite that data using less space.
This isn't just a neat trick; it’s fundamental to how we share and consume media. This process of shrinking files for streaming and storage is a huge topic on its own. If you want to dive deeper, this article on what video encoding is is a great place to start.
The end goal is always the same: reduce the file size. Doing so unlocks some immediate and seriously practical benefits:
- You save tons of storage space. Smaller files mean you can fit way more on your laptop, your phone, or your cloud drive.
- Sharing becomes way faster. A 10 MB file zips across email or Slack in seconds, while a 100 MB one can feel like an eternity.
- Websites load much quicker. For creators, this is huge. Compressed images and videos are the secret to a snappy website, which keeps visitors happy and even helps with SEO.
- It cuts down on costs. Less storage and less bandwidth used for transfers can lead to real savings, especially for businesses.
Two Core Approaches
There are two main philosophies when it comes to shrinking files: lossless and lossy. They sound similar, but the difference is critical.
Lossless compression is the perfectionist. It reorganizes the data without throwing a single bit away. When you open the file again, it’s a perfect, bit-for-bit reconstruction of the original. Zero quality is lost. This is non-negotiable for things like text documents, source code, or master audio and video files where every piece of data is essential.
Then there's lossy compression, the pragmatist. It achieves much, much smaller file sizes by permanently deleting data that our human eyes and ears are unlikely to miss. This is the go-to method for photos, music, and videos, where sacrificing a tiny, imperceptible amount of quality is a fantastic trade-off for a dramatically smaller file.
Compressed vs Uncompressed Files At a Glance
To make it even clearer, here’s a quick table breaking down the key differences between a file in its original state and its compressed version.
| Characteristic | Uncompressed File | Compressed File |
|---|---|---|
| File Size | Large; retains all original data. | Significantly smaller. |
| Quality | Perfect, original fidelity. | Can be identical or slightly reduced. |
| Storage Needs | Requires maximum disk space. | Minimized, freeing up valuable storage. |
| Transfer Speed | Slow to upload, download, and share. | Fast and efficient for sharing and streaming. |
| Use Case Examples | RAW photos, WAV audio, master video renders. | JPEGs for web, MP3s for music, ZIP archives. |
This side-by-side view really highlights the trade-offs. Uncompressed files are pure and perfect, but compressed files are practical, portable, and efficient for everyday use.
The Two Sides of Compression: Lossless vs. Lossy
When you compress a file, you're at a fork in the road. There are two fundamentally different paths you can take, and your choice hinges on a simple trade-off: do you need perfect, pixel-for-pixel quality, or are you chasing the smallest possible file size?
Understanding this difference is everything for creators managing digital assets. The two methods are called lossless and lossy compression. Think of them as two different ways of packing a suitcase for a trip.
Lossless Compression: Perfect Reconstruction
Lossless compression is like being a meticulous packer. You carefully fold every shirt, roll every pair of socks, and fit everything into your suitcase so it takes up less space. When you arrive at your destination and unpack, every single item is exactly as it was before you packed it—just more efficiently arranged.
This method works by finding repetitive patterns in the data and creating a kind of shorthand to represent them. Not a single bit of the original information is thrown away. When you open the file later, the software uses that shorthand to perfectly reconstruct the original data, ensuring 100% quality retention.
Lossless is non-negotiable when every last detail is sacred. It's the only choice for things like text files, application source code, or master archive files where even a tiny, single-bit change would corrupt the entire thing.
Lossy Compression: Smart Sacrifices
Lossy compression is a bit more pragmatic. It’s like rolling your clothes instead of neatly folding them. Sure, you might end up with a few minor wrinkles (which is our analogy for tiny bits of data loss), but you can cram way more into that suitcase, making it much lighter and smaller.
This technique works by permanently removing bits of data that our own eyes and ears are unlikely to even notice. A lossy algorithm might look at a photo of a clear blue sky, identify thousands of slightly different shades of blue, and decide to simplify them into just a few hundred shades. The change is virtually invisible to the human eye, but the file size reduction is massive, often shrinking files by 80-90% or more.
- Perfect for Media: Lossy is the undisputed king for web images, streaming video, and digital audio where small file sizes are critical for fast delivery.
- The Quality Trade-off: The more you compress, the more data gets tossed out. Push it too far, and you’ll start seeing visual messiness (called "artifacts") or hearing a drop in audio clarity.
Lossless vs. Lossy Compression Compared
So, which one is right for you? It all boils down to your goal. Are you archiving a master copy for the ages, or are you prepping an image for a fast-loading webpage? The table below lays out the core differences to make the decision clearer.
| Attribute | Lossless Compression | Lossy Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | No data is ever lost. The file can be restored to its exact original state. | Data is permanently removed to reduce file size. |
| File Size Reduction | Moderate reduction (typically 20-50%). | Significant reduction (often 80% or more). |
| Best Use Cases | Text documents, code, master files, medical images, technical drawings (e.g., ZIP, PNG, FLAC). | Web photos, online video, streaming audio, digital distribution (e.g., JPEG, MP3, H.264). |
| Key Principle | Finds and replaces redundancy without discarding information. | Intelligently removes data that is least perceptible to humans. |
Ultimately, choosing between lossless and lossy is a strategic decision. Both are powerful tools, and knowing when to use each one is the key to managing your digital assets like a pro.
How Algorithms Shrink Your Files
At the heart of every compression tool is a clever set of rules called an algorithm. You can think of an algorithm as a specific recipe for shrinking data and then, just as importantly, putting it back together again. It’s the engine that powers the whole process, dictating exactly how to find and remove repetitive or unnecessary information without turning your file into a jumbled mess.
Different algorithms are designed for different kinds of data. Some are brilliant at spotting repeating patterns in text, while others are masters at simplifying the complex color information in a photograph. This leads us to the two main strategies they use: lossless and lossy compression.
The Lossless Strategy: Finding Patterns
The lossless approach is all about creating a clever shorthand for repetitive information.
Imagine you're writing a document that uses the long phrase "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" over and over. A lossless algorithm would scan the text, notice this pattern, and replace every single instance with a short, unique placeholder, like ~1.
It then creates a tiny dictionary for the file that simply says ~1 = "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." When you decompress the file, the algorithm just reverses the process, swapping every ~1 back to the full phrase. The result is a perfect, bit-for-bit reconstruction of the original. This is the magic behind everything from ZIP archives to PNG images.
The Lossy Strategy: Smart Simplification
Lossy algorithms take a completely different, and arguably more daring, approach. They work by permanently throwing away data that our eyes and ears are unlikely to notice anyway.
Picture an artist painting a vast blue sky. Instead of meticulously using thousands of subtly different shades of blue, they might just use a handful of representative shades that still capture the overall look and feel.
This is exactly what a JPEG algorithm does. It analyzes blocks of pixels, averages out similar colors, and gets rid of fine-grained details that are tough for the human eye to perceive. You lose some of the original information forever, but the file size shrinks dramatically. The key is that the sky still looks like a sky, and for most everyday uses, that trade-off is more than worth it.
If you want to dive deeper, you can learn more about these different data compression methods and the specific algorithms that power them.
This decision tree helps visualize the choice between perfect quality and maximum efficiency.
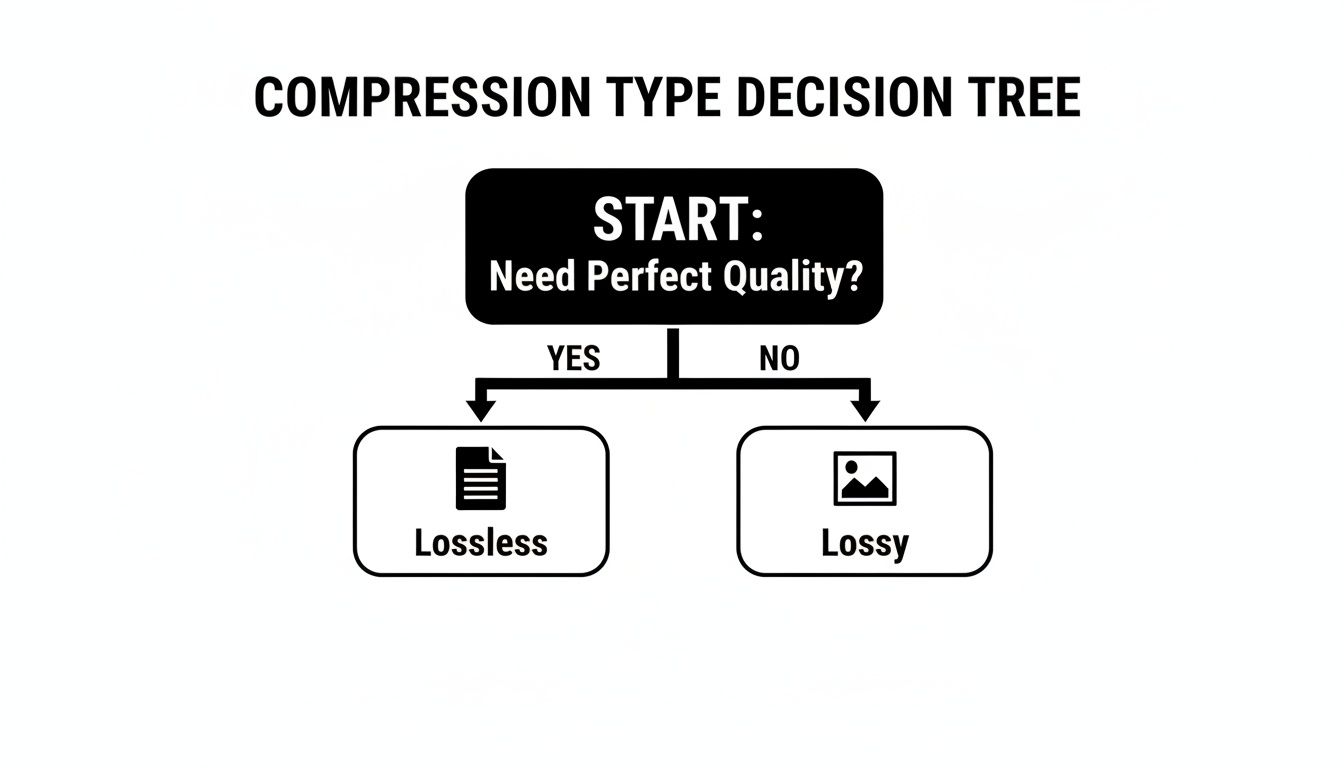
The flowchart makes the choice clear: if you absolutely cannot afford to lose a single bit of data, lossless is your only option. For almost everything else, lossy compression will give you a much smaller file.
Common File Formats and the Compression They Use
Now that we’ve got the theory down on lossless versus lossy compression, let’s see how it plays out in the real world with the files you use every single day. When you choose a file format, you're often unknowingly choosing a specific type of compression, each one fine-tuned for a particular job.
This is where abstract ideas like algorithms and data reduction become practical tools. From photos and videos to documents and archives, picking the right format can make a massive difference in both quality and file size.
Image Formats JPEG vs PNG
When it comes to images, the two heavyweights you'll run into are JPEG and PNG. They’re a perfect real-world example of the lossless vs. lossy showdown.
-
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): This is the king of photos for a reason. JPEGs use lossy compression to get file sizes down to a fraction of the original. The algorithm is brilliant at tossing out subtle color and light details your eyes likely won't notice anyway, making it perfect for complex images with tons of gradients, like photographs.
-
PNG (Portable Network Graphics): This format is all about lossless compression. It’s the go-to for anything that needs to stay perfectly crisp: logos, icons, text, and graphics with transparent backgrounds. It preserves sharp edges and solid blocks of color flawlessly. The trade-off? You get perfect quality, but the file sizes are usually much larger than JPEGs.
Choosing between JPEG and PNG is a classic creative decision. For that rich, detailed photograph on your website, a well-compressed JPEG is your best bet. But for your company logo that needs to look razor-sharp on any background, PNG is the only way to go.
Video Codecs H.264 and H.265
Video files are notoriously huge. They lean heavily on sophisticated lossy compression algorithms—called codecs—to make them small enough to stream and share without bringing your internet to a crawl.
The most common codec, H.264 (AVC), works by analyzing motion between frames. Instead of storing every single pixel of every frame, it saves one full frame (called an I-frame) and then just records the changes that happen in the frames that follow. It’s a clever trick that leads to massive size reductions with very little visible loss in quality.
Its successor, H.265 (HEVC), is even smarter. It delivers roughly the same visual quality at about half the file size, which is what makes it possible to stream 4K video without it buffering every five seconds.
Archives and Documents ZIP and PDF
Compression isn’t just for media. The documents and archives we use daily also rely on smart compression to stay nimble and efficient.
-
ZIP: The humble ZIP file is a classic example of lossless compression. It uses an algorithm called DEFLATE to bundle one or more files into a single, smaller package. This need for lossless compression comes from the early days of computing when every byte of storage was precious. Innovations like the DEFLATE algorithm, which cleverly combines LZ77 and Huffman coding, made it possible to shrink text files by 50-70% without losing a single character.
-
PDF (Portable Document Format): PDFs are the ultimate hybrid. They use a mix of compression techniques to get the best of both worlds. Text and vector graphics are often compressed losslessly to keep them perfectly clear, while any images embedded inside the document are usually hit with a lossy method like JPEG to keep the overall file size manageable. If you work with different kinds of archives, you might be curious how they stack up; we break it all down in our guide on 7-Z vs. ZIP. This balanced approach is what makes the PDF format so flexible and efficient for sharing complex documents.
Putting Compression to Work in Your Creative Workflow
Understanding the theory is one thing, but making file compression a seamless part of your daily creative process is where the real magic happens. For creators, efficiency isn't just about shaving off a few seconds; it's about reclaiming valuable time and energy. The good news is that modern tools can transform this once-tedious task into an effortless, almost invisible step.
Imagine you’ve just wrapped a photoshoot and need to prep 200 high-resolution images for a client preview. Instead of the soul-crushing task of exporting each one manually, you can use batch processing. Just drag the entire folder of images into a compression app, set your rules, and let it do the heavy lifting while you grab a coffee.
Streamlining with Presets and Automation
Consistency is the hallmark of professional work, and this is where presets become your best friend. You can create and save specific compression settings tailored for different needs—one for web graphics, another for social media videos, and a third for email attachments.
Using presets means every asset you export meets the exact same quality and file size standards. It removes the guesswork and helps maintain brand consistency across all your projects.
This ensures your website’s hero images are always crisp but lightweight, and your Instagram videos upload without a hitch. Applying the right compression is crucial when managing media, like when you're resizing videos for different platforms.
You can push this efficiency even further with powerful automation. Some tools let you set up a "watched folder" on your Mac. Any file you drop into that folder is automatically compressed and moved to a destination of your choice. It's a completely hands-off system, perfect for handling routine tasks like optimizing screenshots or prepping assets for a CMS.
The Power of Local Processing
In an age of cloud-based everything, there’s a quiet power in keeping your work on your own machine. Local compression gives you a huge advantage in security and privacy. Your sensitive client files, proprietary designs, or unreleased video projects are never uploaded to a third-party server. The entire process happens directly on your Mac, giving you total control and peace of mind.
This approach builds on the same principles of efficiency that have shaped digital media for decades. The JPEG format, for example, transformed digital photography with its clever use of the discrete cosine transform (DCT) to discard details the human eye can't see. This innovation made images portable and fueled the rise of digital cameras and social media. You can dive deeper into this history on Wikipedia's data compression page.
Modern desktop tools carry on this legacy, delivering impressive size reductions in seconds. Tracking these savings can be incredibly motivating—seeing exactly how many gigabytes of disk space you’ve reclaimed makes it easy to justify better practices across your entire team.
Seeing the Real World Impact of Smart Compression
Theory is one thing, but seeing file compression solve actual problems is where its value really clicks. The savings aren't just abstract numbers; they translate directly into faster workflows, happier users, and lower costs. Let's look at a few concrete examples of smart compression in action.
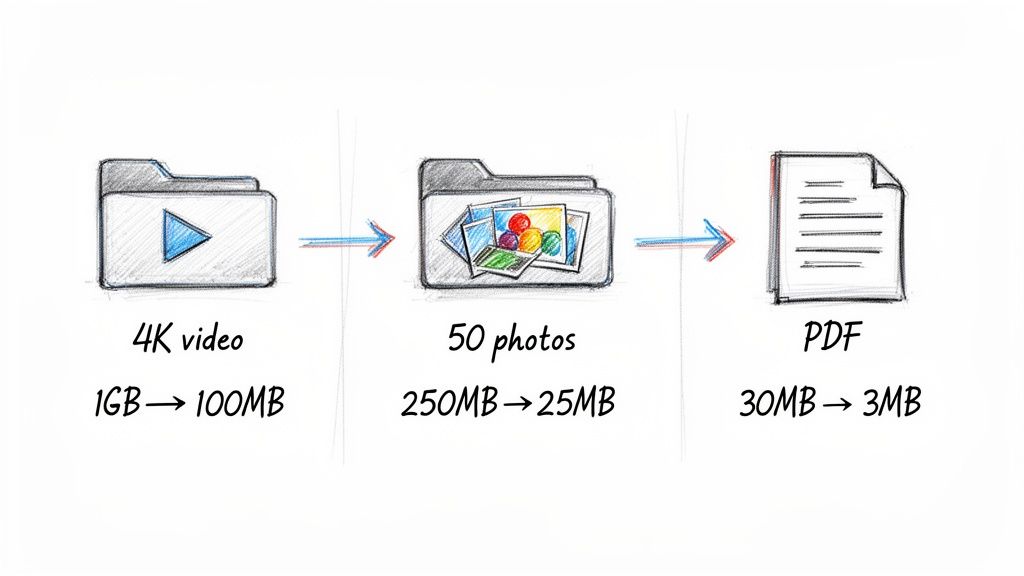
From Gigabytes to Megabytes
Imagine a video editor just finished a 1 GB 4K clip for a new social media campaign. Uploading a file that massive would be painfully slow, and many platforms would reject it outright. But by using a modern video codec like H.265 (HEVC), that file can be shrunk down to just 100 MB—a 90% reduction—with no visible loss in quality. This isn't just a convenience; it’s what makes today's video-driven internet possible.
Video codecs have come a long way. Giants like Netflix rely on standards like H.264 to slash their bandwidth needs by up to 90%. The latest H.265 codec pushes that efficiency even further, which is critical considering video is projected to make up 82% of all internet traffic by 2025. It’s amazing to see how far video compression has come since the early days.
When you compress your assets, you're not just saving space. You’re making your content more accessible, your website faster, and your entire workflow more efficient. These small optimizations lead to huge gains in productivity and user engagement.
Enhancing E-commerce and Document Sharing
This same principle applies to every digital asset you create. An e-commerce store with 50 high-resolution product photos, totaling 250 MB, can compress them into a nimble 25 MB batch. That simple step dramatically speeds up page load times, a critical factor for keeping customers engaged and boosting SEO rankings.
Likewise, a detailed 30 MB PDF user manual can be compressed down to a lightweight 3 MB file. Suddenly, it's effortless to attach to an email or share in a support chat, smoothing out customer communication. These examples show how compression directly impacts business operations, revealing many benefits of file compression that go far beyond just saving a little disk space.
A Few Common Questions About Compression
Even with a solid grasp of the basics, some practical questions always pop up when you start applying this stuff to your everyday work. Let's clear up a few of the most common ones so you can move forward with confidence.
Can a File Be Compressed More Than Once?
Technically, yes, but you almost never should. Trying to re-compress a lossy file that's already been compressed, like a JPEG, is a recipe for disaster. Each time you do it, you throw away more data, and the quality loss can become painfully obvious.
For lossless formats like a ZIP archive, compressing it again usually accomplishes next to nothing—you won't see any meaningful size reduction.
It's always best practice to work from the original, high-quality source file. Apply compression just once to achieve your final, desired output settings.
Does Compressing a File Change Its Type?
That depends entirely on what you're doing. If you're simply archiving files into a .zip container, you're just bundling them together. The original file types inside stay exactly as they were.
However, if you're converting a file from one format to another, then yes, the type changes. Think of it like this:
- Saving a lossless TIFF image as a lossy JPEG is an act of compression that also changes the file extension from .tiff to .jpg.
- Re-encoding a video to a more efficient codec like H.265 fundamentally alters its internal structure and format.
What Are the Downsides of File Compression?
Everything's a trade-off, right? With lossy compression, the biggest downside is the permanent loss of data. If you get too aggressive with the settings, you can seriously degrade the quality of your image or video.
With lossless compression, the main drawback is that the file size reduction is much less dramatic. You also have to account for a tiny bit of computational cost—your machine needs a little processing power to compress and decompress the files on the fly.
Ready to put these concepts into practice? Compresto is the ultimate tool for macOS that makes file compression fast, easy, and secure. Compress videos, images, and PDFs with a simple drag-and-drop, reclaiming storage space and speeding up your workflow. Get started at https://compresto.app.