8 File Management Best Practices for 2025
Taming the Digital Chaos: Mastering Your Files
Drowning in files? This listicle presents eight file management best practices to reclaim control and boost your productivity. Learn how to establish a logical folder hierarchy, implement consistent file naming conventions, and perform regular cleanups. Discover effective version control, backup strategies, cloud storage solutions, and security protocols. We'll also cover optimizing file formats and compression for Mac users and content creators seeking quality-preserving file size reduction. Master these file management best practices and safeguard your valuable data.
1. Establish a Logical Folder Hierarchy
One of the most fundamental file management best practices is establishing a logical folder hierarchy. This involves organizing your files and directories in a structured, hierarchical manner, much like a family tree. A well-defined folder structure acts as a roadmap to your digital assets, enabling you to quickly locate specific files, improving collaboration, and streamlining workflows. Implementing this practice significantly contributes to efficient file management, which is crucial for both individual productivity and organizational success.
This method works by categorizing files based on shared characteristics, such as project, date, client, or content type. These categories become the top-level folders. Subsequent levels provide increasing granularity, narrowing down the scope until you reach the individual files. This hierarchical structure with clear categories, subcategories, and standardized naming conventions is the backbone of effective file management. A hierarchy with no more than 3-4 levels deep is usually optimal for easy navigation. For example, a project-based hierarchy might look like /Projects/ProjectName/Year/Deliverables/, keeping the levels concise and easy to navigate.
Successful implementations of folder hierarchies can be seen across various industries. Microsoft, for instance, often uses a project-based hierarchy: /Projects/ProjectName/Year/Category/. Adobe Creative teams might organize by: /Client/Campaign/AssetType/Version/. Law firms, with their document-heavy workflows, typically use a structure like /Client/Matter/DocumentType/Year/. These examples highlight the adaptability of this method to various professional needs.
The following infographic visualizes a simplified three-level folder hierarchy. This diagram illustrates the hierarchical relationships between a top-level 'Category', a mid-level 'Subcategory', and a bottom-level 'Project/Version', reflecting the logical structure recommended for effective file organization.
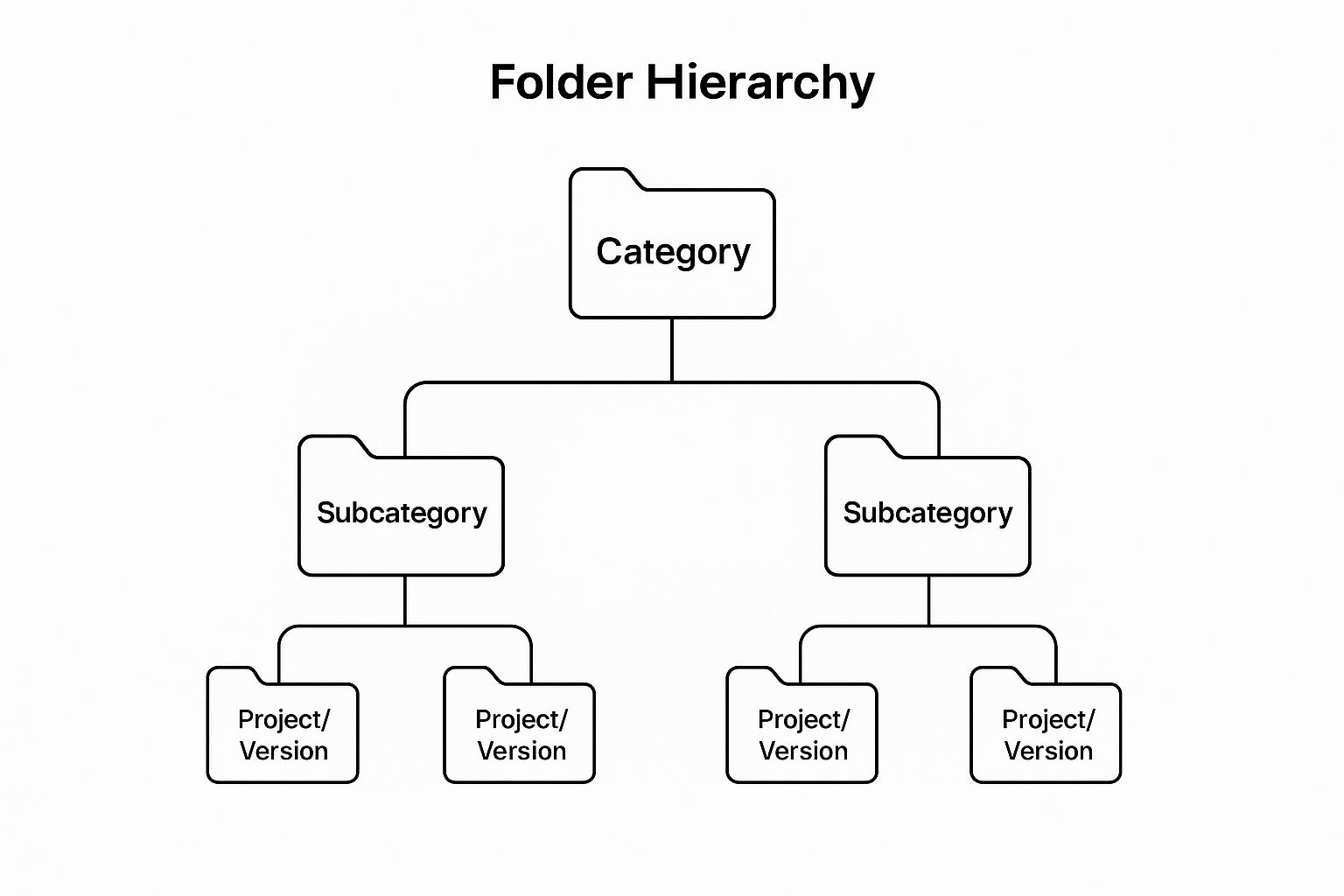
As the infographic illustrates, the cascading structure ensures that each file resides within a specific context, simplifying navigation and retrieval. By starting with broad categories and adding more specific subcategories and projects/versions, you create a well-organized system that’s easy to navigate.
Here are some actionable tips to build a robust folder hierarchy:
- Start broad, get specific: Begin with broad categories and progressively add more specific subcategories as needed.
- Action-oriented names: Use action-oriented folder names (e.g., 'To Review', 'In Progress', 'Complete') for better workflow management.
- Consistency is key: Maintain consistent naming conventions across all folders. Avoid special characters and spaces in folder names.
- Document your system: Create a shared guide outlining your folder structure and naming conventions to ensure team consistency.
- Periodic review: Regularly review and restructure your hierarchy as your needs evolve and your data volume grows. This ensures your system remains scalable and efficient.
The benefits of a well-organized folder hierarchy are numerous. It drastically reduces the time spent searching for files, a common productivity drain. It improves team collaboration and handoffs by providing a shared understanding of where information resides. A logical structure also enables faster backup and archival processes. Furthermore, it supports better version control, particularly important for creative professionals and software developers.
While the advantages are clear, implementing a logical folder hierarchy does require an initial time investment to set up. Maintaining consistency, especially across large teams, can also be a challenge. And as projects and priorities change, periodic restructuring might be necessary. However, the long-term benefits in terms of improved efficiency and reduced frustration far outweigh these initial hurdles. Learn more about Establish a Logical Folder Hierarchy to delve deeper into best practices and advanced strategies. This method is highly recommended for anyone dealing with large volumes of digital files and seeking to improve their file management best practices, especially corporate professionals, Mac users, and content creators who need a structured and accessible system.
2. Implement Consistent File Naming Conventions
One of the cornerstones of effective file management is implementing consistent file naming conventions. This practice involves establishing a standardized system for naming files that incorporates relevant metadata such as dates, version numbers, project codes, and descriptive content identifiers. By embedding this crucial information directly into the file name, you make files immediately identifiable and easily sortable without having to open them, saving valuable time and reducing frustration. This structured approach transforms chaotic folders into organized repositories of information, streamlining workflows and boosting productivity.

A well-defined file naming convention acts as a roadmap to your digital assets. Imagine trying to locate a specific image from a photoshoot with hundreds of files simply named "IMG_001," "IMG_002," and so on. Now imagine those same files named using a convention like "2024-07-27_ClientName_ProductShoot_IMG_001_v1." The difference is stark. The latter provides context, enabling quick identification and eliminating the need to preview each file. This systematic approach significantly improves searchability, making it easier to locate files across different systems and platforms.
A robust file naming convention usually incorporates several key features. Date formatting, typically YYYY-MM-DD, allows for chronological sorting, presenting files in a logical order. Version control indicators, such as v1.0, v2.1, or FINAL, eliminate confusion about the current version of a document, ensuring everyone works with the most up-to-date file. Project or client codes offer immediate identification of the relevant project, particularly helpful when dealing with multiple clients or projects simultaneously. Finally, descriptive but concise content identifiers provide a brief summary of the file's contents.
The benefits of implementing consistent file naming conventions are numerous. Files automatically sort chronologically and logically, significantly reducing time spent searching. Version control becomes seamless, minimizing errors and ensuring everyone is on the same page. Searchability across various systems is dramatically improved, making it easy to locate files regardless of their location. Moreover, structured naming reduces the risk of duplicate file creation, a common problem that can lead to version control nightmares. Learn more about Implement Consistent File Naming Conventions
However, maintaining a consistent naming convention does require discipline and training. Team members need to be educated on the chosen system and adhere to it rigorously. Longer file names can sometimes result from incorporating all the necessary metadata. Additionally, the specific naming convention may need adjustment for different file types or project requirements. For instance, video files might require additional metadata related to resolution or frame rate.
Several organizations have successfully implemented file naming conventions to streamline their operations. Google, for example, utilizes an internal standard often resembling YYYY-MM-DD_ProjectCode_DocumentType_v#. NASA uses a system like Mission_Instrument_Date_SequenceNumber_Version, tailored to their specific needs. Design agencies frequently adopt conventions such as Client_Project_AssetType_Date_Version. These real-world examples showcase the adaptability and effectiveness of structured file naming.
To implement a successful file naming convention within your team or organization, consider these actionable tips: Use leading zeros for numbers (01, 02, 03) to ensure proper sorting. Avoid spaces and use underscores or hyphens instead. Keep names under 255 characters for system compatibility. And finally, create naming convention templates for different document types to maintain consistency across various file formats. This ensures everyone understands the system and can easily apply it to their work.
Adopting consistent file naming conventions is a fundamental best practice in file management. Whether you are a corporate professional handling sensitive client data, a Mac user seeking streamlined organization, or a content creator managing a vast library of assets, this method provides a powerful solution. By investing the time and effort to implement a robust naming system, you will reap the rewards of improved efficiency, reduced frustration, and enhanced collaboration. This seemingly small change can have a profound impact on your overall productivity and workflow.
3. Regular File Cleanup and Archival
Effective file management isn't just about organizing existing files; it's also about proactively managing their lifecycle. Regular file cleanup and archival is a crucial aspect of file management best practices, ensuring that your system remains efficient, storage costs are controlled, and valuable data is preserved for the long term. This systematic approach involves reviewing, organizing, and removing outdated or unnecessary files while simultaneously archiving important historical data. This practice maintains system performance and ensures storage resources are used efficiently while preserving valuable information for future use.

This method operates on a cyclical basis, with scheduled reviews occurring monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the volume of data and the organization's specific needs. The process relies on establishing clear criteria for determining which files should be deleted and which should be archived. These criteria might be based on file type, age, last access date, or relevance to ongoing projects. Leveraging automated tools can significantly streamline this process, helping identify old, unused, or duplicate files quickly. A tiered storage approach – utilizing active storage for frequently accessed files, archive storage for less frequently used data, and cold storage for rarely accessed historical information – further optimizes resource allocation and cost efficiency.
For corporate professionals seeking efficient file management solutions, a well-defined cleanup and archival process is indispensable. It reduces storage costs, improves search efficiency, and streamlines backup procedures. Content creators requiring quality-preserving file size reduction also benefit from regular cleanup, freeing up valuable storage space on their devices and in the cloud. For Mac users looking for advanced file compression and archival solutions, incorporating these best practices can greatly enhance their workflow.
Successful implementation of this method can be seen across various industries. For instance, Amazon Web Services utilizes automated systems to move infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage tiers, optimizing costs without sacrificing data availability. Legal firms, bound by regulatory requirements, typically archive case files after a specific period, often seven years. Design agencies, on the other hand, might archive project files quarterly, ensuring that only active projects occupy readily accessible storage.
This approach boasts a number of advantages. It improves system performance by reducing the volume of data active storage needs to handle. Lower storage costs are a direct result of moving less frequently accessed data to more economical storage tiers. Finding current files becomes easier when outdated information is removed or archived. Backup times are reduced, and backup processes are simplified. Crucially, regular file cleanup and archival helps ensure compliance with data retention policies. You can Learn more about Regular File Cleanup and Archival for in-depth information on data archiving best practices.
However, it's crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks. There's always a risk of accidentally deleting important files, particularly without a well-defined process and clear criteria. The process requires a time investment for regular maintenance and review, though this is often offset by the long-term efficiency gains. In some organizations, deletion decisions may require approval processes, adding another layer of complexity.
To implement regular file cleanup and archival effectively, consider these actionable tips:
- Create a cleanup checklist: Develop a detailed checklist with specific criteria for each file type within your organization. This will ensure consistency and reduce the risk of accidental deletion.
- Use metadata: Leverage file age and last access date metadata to guide your decisions. This provides objective criteria for determining a file’s relevance.
- Implement a staging area: Create a "staging" area or folder for files pending deletion. This provides a safety net, allowing for retrieval of mistakenly deleted files within a specific timeframe.
- Set calendar reminders: Schedule regular cleanup sessions and set calendar reminders to ensure the process is consistently maintained.
By integrating regular file cleanup and archival into your file management strategy, you can ensure optimal system performance, efficient storage utilization, and the preservation of valuable data for years to come. This practice deserves its place among file management best practices because of its impact on both immediate efficiency and long-term data integrity.
4. Version Control and File History Management
Version control and file history management are crucial file management best practices for anyone working with evolving documents or projects. This systematic approach tracks changes, maintains various file versions, and preserves the complete evolution of your work, offering a safety net against errors and facilitating seamless collaboration. It encompasses both manual techniques, such as meticulously naming files with version numbers, and sophisticated automated systems like Git, which are now industry-standard. Embracing a robust version control system can significantly enhance your productivity, reduce the risk of data loss, and streamline collaborative workflows.
At its core, version control is about creating a chronological record of changes to a file or project. This involves storing multiple versions, each representing a specific point in its development. Imagine you're drafting a crucial proposal. Instead of overwriting the same file repeatedly, version control allows you to save distinct iterations, such as “Proposal_v1.0,” “Proposal_v1.1,” and “Proposal_v2.0.” This simple example demonstrates manual versioning, which, while helpful, can become cumbersome for complex projects.
This is where automated version control systems (VCS) come into play. A VCS automatically tracks and manages different versions of your files, allowing you to revert to previous states, compare changes, and even merge modifications from multiple contributors without the nightmare of conflicting edits. These systems typically use a clear version numbering system, often following the semantic versioning format (major.minor.patch), to identify different iterations. For instance, version 1.2.3 represents a minor update (2) to the first major release (1) with a small patch (3).
Implementing version control has numerous benefits. It enables recovery from mistakes by allowing you to easily revert to an earlier version. Imagine accidentally deleting a critical section of your proposal – with version control, retrieving the previous version is a simple process. This feature significantly reduces anxiety about experimenting with different ideas, as you know you can always go back.
Collaboration also becomes dramatically more efficient with version control. Multiple individuals can work on the same project simultaneously without fear of overwriting each other's changes. The VCS tracks each contributor's modifications and provides tools to merge them seamlessly. This eliminates the frustrating back-and-forth of emailing different file versions and manually resolving conflicts.
Furthermore, version control provides a comprehensive audit trail, documenting every change made to a document or project. This is invaluable for important documents where tracking modifications is essential, such as legal agreements or design specifications. You can easily see who made a change, when they made it, and what the change entailed.
However, version control is not without its drawbacks. One primary concern is storage space. Storing multiple versions of files, especially for large projects, can consume significant disk space. Another challenge is maintaining discipline. Consistently committing changes and adding meaningful comments requires diligent practice. Without this discipline, the version history can become confusing and lose its value. Finally, multiple versions can sometimes create confusion about which version is the most current or “official.” Clear communication and established protocols are essential to avoid this confusion.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of version control far outweigh the disadvantages, making it an essential file management best practice. Numerous real-world examples demonstrate its effectiveness. Virtually all software development teams rely on Git, a distributed version control system popularized by GitHub, for managing their codebase. Microsoft Office 365 offers automatic version history for documents, allowing users to track changes and restore previous versions. Adobe Creative Cloud incorporates version management for design files, and contract management systems utilize versioning for legal documents. These are just a few examples of how version control is being used across various industries to improve workflow and safeguard valuable data.
To effectively implement version control, consider these practical tips: Never edit original files directly; always work on copies. Use "FINAL" sparingly in version names, as it can be misleading. Include brief but informative change notes in version comments to provide context for future reference. Establish clear rules about who can create and approve “official” versions to avoid confusion.
By implementing version control as a core file management best practice, individuals and teams can dramatically improve their productivity, minimize the risk of data loss, and foster a more collaborative and efficient work environment. From simple manual techniques to sophisticated automated systems, the benefits of version control are undeniable, contributing significantly to a more organized and productive workflow.
5. Implement Robust Backup and Recovery Systems
Among the most critical file management best practices is implementing a robust backup and recovery system. This isn't just about occasionally copying files to a USB drive; it's about developing a comprehensive strategy that safeguards your valuable data against a range of potential threats, from hardware failures and accidental deletions to natural disasters and cyberattacks. A well-designed backup and recovery system ensures business continuity, protects intellectual property, and provides peace of mind knowing your critical work is safe. This is why it's a cornerstone of effective file management best practices.
This approach revolves around the 3-2-1 backup rule, a widely accepted standard for data protection. This rule dictates maintaining three copies of your important data on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite. Let's break this down:
- Three Copies: This redundancy ensures that even if one or two backups fail, you still have access to your data. The original files on your working device count as the first copy.
- Two Different Media Types: Diversifying your storage media protects against the failure of a specific technology. For example, you might use an external hard drive and cloud storage. This prevents a single point of failure.
- One Offsite Copy: This protects against physical threats like fire, theft, or natural disasters that could destroy all your local backups. Cloud storage or a hard drive kept at a different location fulfills this requirement.
Implementing a robust system involves leveraging several key features:
- Multiple Backup Locations: Utilizing a combination of local (external hard drives, NAS devices), cloud (services like Google Drive, Dropbox, Backblaze), and potentially offline storage (physical media like tapes or write-once disks for archiving) ensures comprehensive protection.
- Automated Backup Scheduling: Software solutions allow you to schedule automatic backups at regular intervals (daily, weekly, or even hourly), eliminating the risk of forgetting to manually back up your files. This consistency is crucial for maintaining up-to-date backups and minimizing potential data loss.
- Regular Backup Verification and Testing: It's not enough to simply create backups; you must regularly verify their integrity and test the recovery process. This confirms that your backups are working correctly and that you can restore your data in case of an emergency. This testing should include restoring a small subset of files to ensure they are accessible and uncorrupted.
- Incremental and Differential Backup Options: These techniques optimize backup efficiency by only backing up changes made since the last full or incremental backup, respectively. This saves storage space and reduces backup time.
The advantages of implementing such a system are clear:
- Protection against Data Loss: This is the primary benefit. Whether it's a hardware malfunction, accidental deletion, a ransomware attack, or a natural disaster, a robust backup system ensures your data remains safe.
- Enables Quick Recovery and Business Continuity: Downtime can be costly. A well-designed system allows for swift data restoration, minimizing disruption to your work or business operations.
- Provides Peace of Mind: Knowing your critical data is protected allows you to focus on your work without worrying about potential data loss.
- Automation: Modern backup solutions can be automated, requiring minimal manual intervention after the initial setup.
However, there are also some considerations:
- Ongoing Cost: Cloud storage and backup software often involve subscription fees, and physical storage devices require upfront investment.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: While automation simplifies the process, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure the system functions correctly. This includes checking backup logs, verifying storage space, and updating software.
- Performance Impact: During backup operations, system performance may be slightly impacted, especially with large files or limited bandwidth.
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of robust backup and recovery systems. Pixar famously averted disaster when backups saved Toy Story 2 after it was accidentally deleted. NASA employs multiple redundant backup systems for mission-critical data, ensuring the success of space exploration endeavors. Financial institutions rely on real-time replication to safeguard transaction data and maintain continuous operation.
To maximize the effectiveness of your backup and recovery system, consider these tips:
- Test Your Recovery Process: Don't just test your backups; regularly test the entire recovery process to ensure you can restore your data quickly and efficiently.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Protect your backups with strong encryption to safeguard confidential information in case of unauthorized access.
- Document Your Procedures: Create clear documentation outlining your backup procedures for all team members. This ensures consistency and facilitates recovery in case of staff changes.
- Consider Bandwidth and Time: When scheduling backups, consider the available bandwidth and the time required to complete the process to minimize disruption to network performance.
Implementing a robust backup and recovery system is a non-negotiable aspect of effective file management best practices. By following the 3-2-1 rule, utilizing the available features, and considering the potential drawbacks, you can ensure your valuable data remains safe and accessible, regardless of unforeseen circumstances.
6. Use Cloud Storage and Synchronization Strategically
In today's interconnected world, leveraging cloud storage and synchronization is no longer just a convenient backup solution—it's a crucial component of effective file management best practices. This approach transforms how we interact with our files, enabling seamless access, effortless collaboration, and optimized workflows across multiple devices. By strategically integrating cloud services into your file management strategy, you can unlock significant benefits in terms of productivity, accessibility, and overall efficiency. This involves not just storing files in the cloud, but actively using its features for real-time synchronization, selective access, and streamlined sharing.

Cloud storage platforms function as centralized repositories for your files, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. They employ synchronization mechanisms to ensure that any changes made on one device are automatically reflected across all other connected devices. This real-time synchronization eliminates the need for manual file transfers, drastically reducing the risk of working with outdated versions. Selective synchronization allows you to choose which folders and files are synced to specific devices, optimizing local storage usage. This is particularly useful for users with limited hard drive space who want to keep their most frequently accessed files readily available offline while archiving less critical data in the cloud.
The benefits of implementing cloud storage and synchronization into your file management best practices are numerous. Accessing files from any location with an internet connection offers unparalleled flexibility for remote work and on-the-go access. Automatic synchronization eliminates tedious and error-prone manual file transfers, freeing up time and ensuring data consistency. Furthermore, these platforms provide built-in collaboration and sharing features, facilitating seamless teamwork and efficient feedback loops. By reducing reliance on local storage, cloud storage also allows users to utilize devices with smaller hard drives without compromising access to their entire file library.
Examples of successful implementation abound. Dropbox revolutionized file synchronization for creative professionals, offering a simple and reliable way to share and collaborate on large design files. Google Workspace, with its real-time collaborative document editing capabilities within Google Drive, has become a staple for businesses and educational institutions. Microsoft OneDrive’s tight integration with the Office 365 suite provides a seamless workflow for document creation, editing, and sharing. Box caters to enterprise clients with advanced security and compliance features, addressing the specific needs of businesses handling sensitive data.
However, this approach is not without its drawbacks. A reliable internet connection is essential for full functionality, and ongoing subscription costs for adequate storage can accumulate. Potential security and privacy concerns require careful consideration of provider security measures and data encryption protocols. Simultaneous editing of shared files can create synchronization conflicts, requiring version control mechanisms to avoid data loss or confusion.
To successfully implement cloud storage and synchronization, consider these actionable tips:
- Use selective sync: Optimize local storage by syncing only the files you need regular access to on each device.
- Establish clear sharing permissions: Control access to your files by setting granular permissions for collaborators and reviewing them regularly.
- Monitor sync status: Pay attention to synchronization status icons and notifications to ensure you're always working with the latest file versions.
- Consider bandwidth limitations: Be mindful of large file transfers when working with limited bandwidth to avoid impacting internet performance.
Cloud storage and synchronization deserve a prominent place in any discussion of file management best practices. When used strategically, these services offer a powerful combination of accessibility, collaboration, and efficiency. By understanding the features, benefits, and potential drawbacks, and by implementing the suggested tips, you can effectively leverage cloud storage and synchronization to optimize your file management workflows and enhance productivity. For corporate professionals needing access to files across devices, Mac users looking for extended storage solutions, and content creators requiring seamless collaboration, integrating cloud storage strategically is a vital step in modern file management.
7. Establish File Access Permissions and Security Protocols
Effective file management isn't just about organization; it's also about security. Establishing robust file access permissions and security protocols is a critical file management best practice, ensuring that your data remains confidential, compliant, and protected from unauthorized access. This involves a comprehensive approach to controlling who can access, modify, and share files, whether within an organization's network or on a personal device. This seventh item in our list of best practices is crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of your valuable information.
This method works by implementing a layered security approach. At its core is the principle of least privilege, meaning users are only granted the minimum level of access required to perform their duties. This limits the potential damage from a security breach or accidental data exposure. This principle is put into practice through mechanisms like role-based access control (RBAC), which allows administrators to define roles (e.g., "Marketing Team," "Finance Department") and assign specific permissions to each role. Instead of granting permissions to individual users, RBAC streamlines the process and ensures consistency. For example, the "Marketing Team" role might have read and write access to marketing materials, while the "Finance Department" role has read-only access to those same files but full access to financial records.
Beyond RBAC, robust file security incorporates encryption. File and folder encryption scrambles data, rendering it unreadable without the correct decryption key. This protects sensitive data even if a device is lost or stolen. Additionally, comprehensive audit trails track file access and modifications, providing a record of who accessed what, when, and what changes were made. This is essential for identifying suspicious activity and maintaining accountability. Integration with identity management systems further strengthens security by centralizing user authentication and access control.
The benefits of implementing strong file access permissions and security protocols are substantial. It protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, mitigating the risk of data breaches and their associated financial, legal, and reputational consequences. It also enables compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX, which mandate stringent data protection measures. The detailed audit trails provide accountability, allowing organizations to track file activity and identify potential security vulnerabilities. Finally, this approach allows granular control over file sharing, ensuring that data is shared only with authorized individuals.
However, implementing and maintaining these security measures does have some drawbacks. Increased security can sometimes slow down file access due to the overhead of encryption and authentication processes. The system also requires ongoing management and regular user training to ensure effectiveness. Furthermore, overly restrictive permissions can create barriers to legitimate collaboration and hinder productivity. Therefore, finding the right balance between security and usability is crucial.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of these practices. Healthcare organizations utilize HIPAA-compliant file systems to protect patient medical records. Financial services firms implement SOX compliance measures to secure financial documents. Government agencies employ classified document management systems to safeguard sensitive national security information. Law firms rely on stringent security protocols to protect attorney-client privileged communications. These examples highlight the diverse applications and critical role of robust file security across various sectors.
To effectively implement file access permissions and security protocols within your own file management best practices, consider these actionable tips:
- Follow the principle of least privilege: Grant only the minimum necessary access to users. Regularly review and update permissions to reflect changing roles and responsibilities.
- Use group-based permissions: Assign permissions to groups rather than individual users to simplify management and ensure consistency.
- Implement automatic permission expiration: For temporary access requirements, set expiration dates for permissions to minimize the risk of lingering access.
- Regularly review and audit file permissions: Conduct periodic audits to identify and rectify any discrepancies or potential security vulnerabilities.
- Train users on security best practices: Educate employees on the importance of data security and the proper use of access controls.
By incorporating these file management best practices and prioritizing security, you can create a robust system that protects sensitive information while enabling efficient and compliant collaboration. It’s an essential component of responsible data management in today's increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.
8. Optimize File Formats and Compression
Efficient file management isn't just about organizing; it's also about optimizing. A crucial element of best practices in file management involves strategically selecting and converting file formats and applying appropriate compression techniques. This approach, optimizing file formats and compression, balances quality, compatibility, storage efficiency, and performance requirements, making it an essential skill for anyone working with digital files. Whether you're a corporate professional managing large datasets, a Mac user seeking efficient storage solutions, or a content creator needing to optimize files for distribution, understanding this practice can significantly improve your workflow.
Optimizing file formats and compression involves choosing the right format for a given task and then, if necessary, compressing the file to reduce its size without significantly impacting its usability. This process considers the intended use of the file. For example, a high-resolution image intended for print requires a different format and compression level than an image destined for a website. A raw, unedited video file needs to be stored in a format that preserves all its data, while the version uploaded online needs to be compressed for faster streaming.
How it Works:
The core of this practice lies in understanding the differences between file formats and compression types. Different file formats are designed for different purposes. JPEG is excellent for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, and GIF for simple animations. Similarly, video formats like MP4 and MOV offer varying levels of compression and quality.
Compression techniques fall into two main categories: lossless and lossy. Lossless compression reduces file size without discarding any data. Formats like ZIP, FLAC (for audio), and PNG utilize lossless compression, ensuring that when the file is decompressed, it's identical to the original. Lossy compression, on the other hand, achieves greater size reduction by discarding some data. This is common in formats like JPEG, MP3, and MP4. While lossy compression can significantly reduce file size, it's important to choose a level of compression that balances size reduction with acceptable quality loss.
Successful Implementations:
Many organizations successfully leverage file format optimization and compression. Netflix, for example, uses highly optimized video compression algorithms to deliver high-quality streaming while minimizing bandwidth usage. Photography studios often store original photos in RAW format, which preserves all image data, and then create JPEG versions for clients, balancing quality and file size. Publishing companies frequently use PDF for distributing documents, ensuring consistent formatting across different devices, while maintaining editable source files in formats like DOCX or INDD. Web developers optimize images using formats like WebP, which offers superior compression and quality compared to JPEG, leading to faster website loading times.
Actionable Tips:
- Maintain Uncompressed Masters: Always keep original, uncompressed versions of important files as a master copy. This ensures you have the highest quality version available for future use or editing.
- Use PDF/A for Long-Term Archival: For documents requiring long-term preservation, use the PDF/A format, an ISO-standardized version of PDF designed for archiving.
- Consider File Size vs. Quality Trade-offs: Understand the balance between file size and quality. Higher compression reduces file size but can introduce noticeable artifacts. Choose the appropriate balance based on the intended use.
- Batch Process File Conversions: Utilize batch processing tools or scripts to automate file conversion tasks, especially when dealing with a large number of files. This saves significant time and effort.
- Standardize Formats: Within your organization or team, standardize the file formats used for different purposes. This improves compatibility and streamlines workflows.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Reduced Storage Requirements and Transfer Times: Smaller files take up less space on storage devices and transfer faster across networks.
- Improved Compatibility: Using common formats like PDF ensures accessibility across different systems and software.
- Faster File Loading and Processing: Smaller files load and process faster, improving application performance.
- Significantly Reduced Backup and Sync Times: Smaller files mean faster backups and synchronization processes.
Cons:
- Quality Loss with Lossy Compression: Lossy compression can introduce quality degradation, particularly at higher compression levels.
- Time Required for Conversion Processes: Converting between formats can take time, especially for large files or batches.
- Potential Compatibility Issues with Proprietary Formats: Avoid using proprietary formats whenever possible, as they can create compatibility problems when sharing files.
Optimizing file formats and compression is a vital component of effective file management best practices. By understanding the nuances of different formats and compression techniques, and by applying the tips outlined above, you can significantly improve your workflow, reduce storage costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of your file management system.
8 Best Practices Comparison Guide
| Best Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Establish a Logical Folder Hierarchy | Moderate – initial setup and periodic updates | Low to moderate – planning and documentation | Improved file location speed and collaboration | Teams managing growing file volumes and projects | Faster search, better teamwork, scalable organization |
| Implement Consistent File Naming Conventions | Low to moderate – requires discipline and training | Low – mostly guidelines and templates | Enhanced file identification and sorting | Environments needing version clarity and search | Eliminates confusion, reduces duplicates, easy sorting |
| Regular File Cleanup and Archival | Moderate – scheduled maintenance and criteria | Moderate – time investment and possible tools | Reduced storage costs, faster backups, better compliance | Organizations needing ongoing file management | Improved system performance, storage optimization |
| Version Control and File History Management | High – discipline and possible tool integration | Moderate to high – storage and tools | Reliable tracking of changes, collaboration | Software teams, design projects, legal documents | Recovery from errors, audit trails, conflict reduction |
| Implement Robust Backup and Recovery Systems | Moderate to high – setup and monitoring | High – storage, software, and maintenance | Data protection and quick recovery | Any critical data environment, disaster planning | Prevents data loss, ensures business continuity |
| Use Cloud Storage and Synchronization Strategically | Moderate – setup sync and sharing rules | Moderate – subscriptions and bandwidth | Anywhere access, real-time collaboration | Remote teams, hybrid workflows | Automatic syncing, collaboration, reduced local storage |
| Establish File Access Permissions and Security Protocols | High – ongoing management and training | Moderate – security tools and monitoring | Secure sensitive data, regulatory compliance | Sensitive or regulated data environments | Protects data, audit trails, granular access control |
| Optimize File Formats and Compression | Moderate – format selection and conversions | Low to moderate – software and processing time | Reduced storage and faster transfers | Media-heavy workflows, distribution and archiving | Saves space, improves compatibility, faster loading |
File Management Nirvana: A More Efficient Future
Mastering file management best practices, as outlined above, is crucial for anyone working with digital information. From establishing a logical folder hierarchy and consistent file naming conventions to implementing robust backup systems and leveraging cloud storage strategically, these practices form the foundation of a streamlined and efficient workflow. Regular file cleanup, version control, and secure access protocols further enhance your control and protect your valuable data. Remember, the core components of effective file management involve organization, consistency, and security.
By implementing these file management best practices, you'll not only save time and reduce stress but also improve collaboration, minimize the risk of data loss, and ensure easy access to the information you need, when you need it. Whether you're a corporate professional seeking efficient file management solutions, a Mac user needing advanced file compression tools, or a content creator requiring quality-preserving file size reduction, these principles are universally applicable. Taking control of your digital files empowers you to focus on your core tasks and achieve greater productivity.
For macOS users seeking to further optimize their file management strategy, consider Compresto. Compresto simplifies and streamlines tasks like file compression and conversion, helping you save valuable storage space while preserving file quality. Download Compresto today at Compresto and experience the difference a truly optimized file management system can make.