Difference Between Lossy and Lossless: Complete Compression Guide
The core of the difference between lossy and lossless compression is a simple trade-off: file size versus data integrity. Think of it this way. Lossless compression is like a perfect archivist, carefully preserving every single bit of the original file. The result is a flawless reconstruction, but the file size reduction is modest. On the other hand, lossy compression is a pragmatic editor, strategically cutting out data it deems non-essential to make files dramatically smaller, even if it means a minor—and often unnoticeable—loss in quality.
Understanding the Core Trade-Off
Choosing the right compression method is a decision that directly impacts your storage costs, loading speeds, and the final quality of your assets. The whole point is to shrink the amount of data needed to represent a file, making it far easier to store and quicker to send across the internet. In a world drowning in data, this technology isn't just helpful; it's essential.
The growing importance of smart compression is clear in market trends. The global data compression software market hit USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to nearly double by 2033. This boom is fueled by the non-stop explosion of digital content and our reliance on cloud services.
Lossy vs Lossless At a Glance
To make the choice a bit clearer, let's break down the main differences head-to-head. The table below gives you a quick snapshot of each compression type, helping you match the method to your specific goals.
| Attribute | Lossless Compression | Lossy Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | 100% of original data is preserved. | Some data is permanently removed. |
| Quality | Identical to the original file. | Minor to significant quality reduction. |
| Compression Ratio | Lower (e.g., 2:1 to 3:1). | Much higher (e.g., 10:1 or more). |
| File Size | Larger files. | Significantly smaller files. |
| Reversibility | Fully reversible to the original state. | Irreversible; lost data cannot be recovered. |
| Best Use Cases | Text, code, medical images, archives. | Web images, streaming video, audio. |
The decision really comes down to the situation: Lossless is for fidelity, ensuring every last detail remains intact. Lossy is for efficiency, prioritizing smaller sizes and faster delivery over a perfect carbon copy.
These differences have real-world consequences, especially for web performance. To get a better sense of these practical impacts, it’s worth exploring how lossy and lossless compression affect website speed. Grasping this is key to getting the most out of your digital assets.
When perfect quality is the only thing that matters, lossless compression is the only way to go. Forget about trade-offs—its entire purpose is to preserve a file with absolute, bit-for-bit accuracy.
The way it works is by finding and encoding repetitive data patterns, almost like creating a shorthand for information that shows up over and over. When you decompress the file, the algorithm simply reverses its steps, rebuilding the original data perfectly, right down to the last byte. No quality is lost. No details are changed. No compromises.
The promise of lossless compression is straightforward but powerful: what you put in is exactly what you get out. Every single pixel, character, and data point stays completely intact.
This is precisely why lossless is the undisputed standard for text documents, software applications, and source code. Just imagine a compressed text file where a single letter was altered—the entire meaning could be corrupted. The same goes for software; one wrong bit could make an application completely useless.
Where Data Integrity Is Mandatory
The need for perfect fidelity isn't just about text files. In a lot of professional fields, lossless compression isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a strict requirement for legal, ethical, and operational reasons.
Take healthcare, for instance. Medical imaging files like MRIs or CT scans must be compressed without any data loss. A tiny, seemingly invisible change from lossy compression could hide a critical diagnostic detail, leading to severe consequences for a patient. Financial records, legal contracts, and scientific data sets all fall under this same umbrella where integrity is non-negotiable.

This critical role is reflected in market data. Lossless algorithms are so essential in sectors where data accuracy is everything that the lossless segment now commands approximately 60% of the data compression software market. This is largely driven by its mandatory use in the BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) and healthcare industries, where every bit of information must be preserved for analysis and compliance. You can dig deeper into these market dynamics and the critical role of lossless compression.
Lossless methods make sure a file can act as a master archive—a perfect digital negative that you can open, edit, and save again and again without it ever degrading. This reliability makes it the clear winner for:
- Professional Photography: Photographers use formats like PNG, TIFF, or RAW to keep their master shots pristine, ensuring no quality is lost during editing.
- Data Archiving: ZIP and 7z files use lossless compression to bundle documents and software for storage or transfer, guaranteeing a perfect restoration every time.
- Technical Diagrams: Engineering and architectural plans rely on precise lines and text that can't be altered in any way.
Ultimately, this is where the difference between lossy and lossless becomes crystal clear. When your goal is preservation, not just presentation, lossless is the only path forward.
The Smart Trade-Off of Lossy Compression
Unlike lossless compression, which promises a perfect, bit-for-bit copy, lossy compression makes a much more practical choice. It permanently removes data from a file, but it doesn't just slash away at random. Instead, it uses incredibly sophisticated algorithms that are modeled on human perception to decide what goes.
For images, we call these psychovisual models; for audio, they're psychoacoustic models. Think of it this way: these algorithms are trained to identify and discard the information our senses are least likely to pick up on anyway—like subtle color shifts in a busy photo or quiet sounds hidden behind louder ones. This is where lossy and lossless methods really part ways. Lossy compression sacrifices data you can't perceive for speed you can definitely feel.
The Engine of the Modern Web
This strategic data removal is what allows for massive reductions in file size. It's not uncommon to see compression ratios of 10:1 or even higher. Honestly, this is the engine that makes most of the modern internet work, from Netflix and YouTube delivering smooth 4K video to image-heavy websites loading in a snap. Without it, our digital lives would be a frustrating mess of buffering wheels and slow-loading pages.

The goal is to hit a sweet spot called perceptual transparency. This is where, technically, quality has been lost, but in practice, the average person would never notice. Most tools let you adjust the compression level, so you can dial in the perfect balance between file size and visual quality. Getting good at this is a skill, and exploring different file size reduction tips will help you master it.
The central bargain of lossy compression is simple yet powerful: Sacrifice imperceptible data for tangible speed and efficiency.
It's this trade-off that has cemented lossy compression as the go-to method for nearly all media shared online. The entertainment and media industries are its biggest users, relying on it to cut down on bandwidth, enable smooth streaming, and keep their server costs in check. Because of this, the lossy compression market is growing faster than any other segment, especially for media.
Here's where you'll see it in action every day:
- Web Images: JPEGs and WebP files are compressed heavily to make websites load fast, a critical factor for both user experience and search engine rankings.
- Streaming Media: Services like Spotify and Netflix couldn't exist without lossy audio and video formats like MP3 and MP4 to deliver content without constant buffering.
- Digital Music: Those thousands of songs on your phone? They're almost certainly MP3 or AAC files, which would take up an impossible amount of space if they were uncompressed.
- Social Media: Every photo and video you upload to platforms like Instagram or TikTok is automatically run through a lossy compression algorithm to manage storage and deliver content quickly to millions.
When speed and file size are your top priorities, and you don't need to preserve every last original bit of data, lossy compression is the pragmatic—and almost always the right—choice.
Choosing Your Compression Strategy
Knowing the technical difference between lossy and lossless compression is one thing. Actually applying that knowledge in the real world is another beast entirely. There's no single "best" method—just the right one for the job at hand, and your choice depends completely on the file's purpose and your priorities.
The decision boils down to a trade-off between three key factors: the need for absolute quality, storage or bandwidth limitations, and how you plan to use the file down the road. It’s a practical balancing act. For instance, knowing when to use each method is critical when you need to optimize video for web, ensuring your site loads fast without turning your video into a pixelated mess.
This simple chart breaks down the decision-making process based on what you value most: quality or file size.
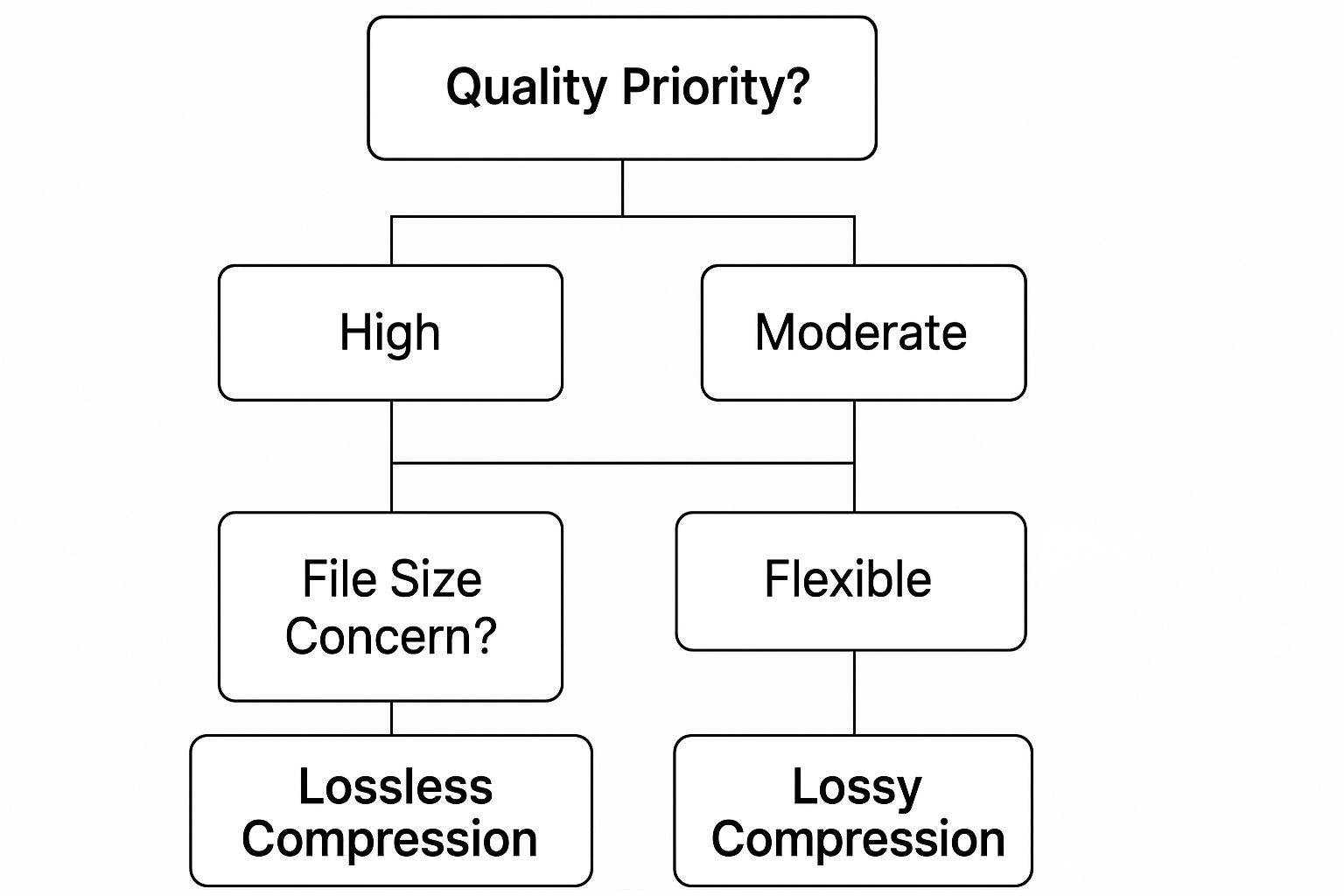
As you can see, it's pretty straightforward. If your main goal is to keep every single bit of original data for pristine, uncompromised quality, then lossless is your only real option, no matter how big the file turns out.
Matching The Method To The Mission
So, let's move from theory to practical, everyday scenarios. Seeing how the lossy vs. lossless choice plays out in the real world is the best way to get a feel for it.
Here’s a quick guide matching common digital tasks with the optimal compression type.
Compression Choice by Scenario
| Scenario | Recommended Compression | Primary Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Archiving Professional Photography | Lossless (e.g., TIFF, RAW) | You need a master file with 100% of the original data for future editing and printing. Quality degradation is unacceptable. |
| Optimizing Website Images | Lossy (e.g., JPEG, WebP) | Fast page load times are critical for user experience and SEO. A small, imperceptible quality dip is a worthy trade-off for speed. |
| Storing Signed Legal Contracts | Lossless (e.g., PDF, PNG) | Absolute data integrity is mandatory. Even a one-pixel change could be legally problematic, so no data can be discarded. |
| Building a Mobile Music Playlist | Lossy (e.g., MP3, AAC) | On-device storage is limited. Sacrificing some inaudible audio frequencies allows you to store thousands of songs instead of hundreds. |
Making the right choice really comes down to thinking about where the file is headed and what its job is.
The core principle is to think about the file's lifecycle. If it's a final-use asset for display, lossy is efficient. If it's a master file for future work or archiving, lossless is essential.
This kind of strategic thinking is crucial. For a deeper dive into techniques for shrinking files without sacrificing your goals, check out our guide on how to reduce file size for professionals. It's packed with practical steps for all sorts of file types.
Ultimately, your choice should always be intentional. Think about the end-user, the storage medium, and the long-term value of the data. For a photographer, their master RAW file is a priceless asset that demands lossless storage, but the JPEG they post on social media is a disposable promotional tool where lossy is perfect. Both choices are correct because they fit the context.
Matching File Formats to Your Needs

Understanding the theory behind lossy and lossless compression is one thing. The real magic happens when you connect that knowledge to the file formats you handle every single day. Each format is built with a specific compression strategy in mind, meaning your choice of file type is a direct trade-off between quality and size.
This moves you beyond just knowing the difference between lossy and lossless and into making smart, practical decisions for your projects. Let's break down the most common formats and the compression methods that make them tick.
Image Formats Demystified
For images, the format you choose has a direct impact on how they look and perform, especially on the web where every kilobyte counts.
- JPEG (or JPG): This is the undisputed king of lossy image compression. It excels at handling complex photos with millions of colors, making it the perfect choice for websites where smaller files mean faster page loads.
- PNG: This format relies on lossless compression. Its standout feature is its ability to preserve every pixel of detail while also supporting transparent backgrounds. This makes it the go-to for logos, icons, and any graphics with sharp lines where quality is non-negotiable.
- WebP and AVIF: These modern formats are incredibly flexible, offering both lossy and lossless compression modes. They often crush older formats in efficiency, delivering much smaller files at the same or even better quality.
Audio and Video Formats
The same principles apply when you're working with media files, where storage space and streaming bandwidth are always top of mind. The choice between lossy and lossless is especially crucial in fields like aerial filmmaking, where footage is often processed with specialized drone video editing software.
The rule of thumb for media is simple: Lossless is for production and archiving. Lossy is for distribution and streaming.
Common Audio Formats
- MP3 and AAC: These are the most widespread lossy audio formats, built for streaming services and your portable music library. They cleverly shed inaudible sound frequencies to achieve impressively small file sizes.
- WAV: Typically an uncompressed format, WAV delivers pure, untouched audio quality but at the cost of enormous file sizes. It's almost exclusively used in professional audio production.
- FLAC: Standing for Free Lossless Audio Codec, FLAC uses lossless compression to shrink files by about 50-70% without discarding a single bit of audio data. It’s the perfect format for archiving your high-fidelity music collection.
Common Video Formats
- MP4: As the universal standard for web video, MP4 uses lossy compression codecs (like H.264 or H.265) to strike an ideal balance between quality and file size for smooth streaming.
- MKV: This is a highly flexible container format that can wrap both lossy and lossless video and audio streams into a single file. You'll often see it used for high-definition movie rips and personal media archives.
Common Compression Questions Answered
When you get deep into file compression, you start running into those tricky edge-case questions. Getting these details right is what separates a smooth workflow from one filled with frustrating mistakes that can degrade your files. Let's clear up a few of the most common points of confusion.
One of the first questions people ask is whether they can turn a lossy file back into a lossless one to get the quality back. The short answer is a firm no. You can technically convert a JPEG into a PNG, but you can't magically recover the data that was permanently thrown away. The conversion just takes the low-quality data and wraps it in a bigger, lossless file container, bloating the file size without any quality boost.
Clarifying Common Scenarios
This leads to another practical question: does zipping an already compressed file, like a JPEG or MP3, actually make it smaller? In most cases, the reduction is so tiny it’s not even worth the effort. Lossy formats are already incredibly compressed, so when you run a lossless algorithm like ZIP over them, there are hardly any new patterns for it to work on.
Think of it this way: trying to zip a JPEG is like trying to vacuum-pack something that's already been shrunk. There's simply not much left for the new compression method to work with.
Finally, what’s the best approach for cloud storage? It really boils down to your goal. If you're archiving master files and need perfect, bit-for-bit integrity, stick with lossless formats like ZIP archives or PNGs. But for everyday access—where you need to balance storage costs and bandwidth—lossy formats like JPEGs and MP3s are far more practical.
Making the right choice also contributes to sustainability; learning how file compression reduces digital waste can help you make smarter, more eco-friendly tech decisions. It's all about striking the right balance between quality, cost, and efficiency.
Ready to take control of your files? Compresto offers powerful, quality-preserving compression for macOS, helping you optimize storage and speed up your workflow. Get Compresto today and see the difference.